
Frost dates vs Heat zones Illustration
Frost dates mark the calendar days when temperatures typically drop below freezing, influencing planting and harvesting schedules for sensitive crops. Heat zones indicate the average number of days per year when temperatures exceed 86degF, affecting plant growth and stress tolerance. Understanding both frost dates and heat zones helps gardeners select suitable plants and optimize watering and care throughout the growing season.
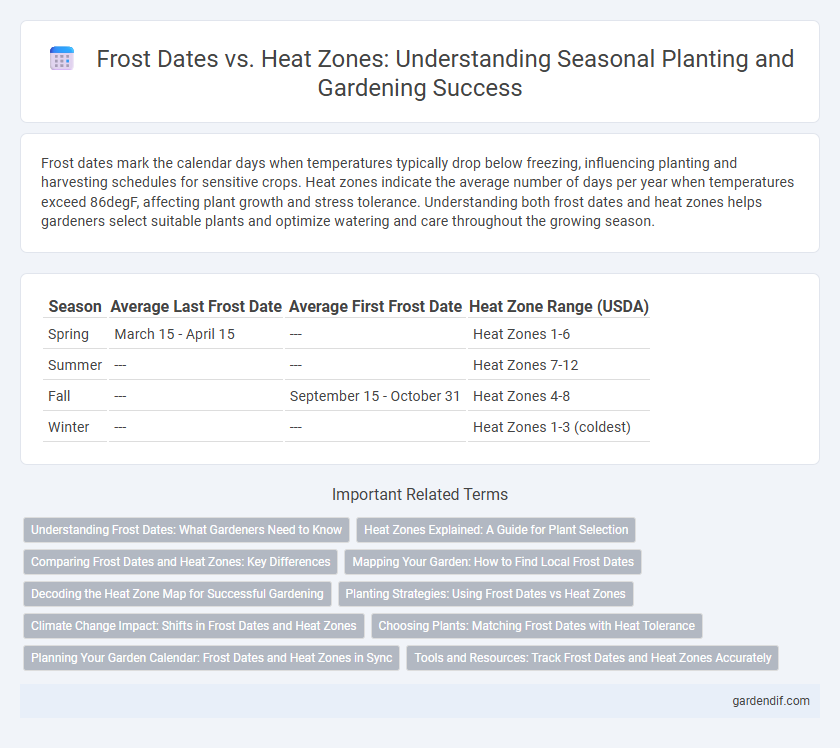
Table of Comparison
| Season | Average Last Frost Date | Average First Frost Date | Heat Zone Range (USDA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | March 15 - April 15 | --- | Heat Zones 1-6 |
| Summer | --- | --- | Heat Zones 7-12 |
| Fall | --- | September 15 - October 31 | Heat Zones 4-8 |
| Winter | --- | --- | Heat Zones 1-3 (coldest) |
Understanding Frost Dates: What Gardeners Need to Know
Understanding frost dates is essential for gardeners to determine the safe planting periods for various crops, as these dates mark the average last and first frost occurrences in a region. Heat zones, which indicate the number of days over 86degF, complement frost dates by helping gardeners select plants that can withstand high temperatures during the growing season. By combining knowledge of frost dates and heat zones, gardeners optimize planting schedules and improve crop survival and yield.
Heat Zones Explained: A Guide for Plant Selection
Heat zones categorize regions based on the number of days with temperatures above 86degF, a critical threshold where plant heat stress occurs. Understanding heat zones allows gardeners to select plants that thrive in specific thermal environments, ensuring optimal growth and reduced heat damage. Unlike frost dates that emphasize cold limits, heat zones provide essential insights into summer and heat tolerance for successful seasonal planting.
Comparing Frost Dates and Heat Zones: Key Differences
Frost dates indicate the average time of the last spring frost and the first fall frost, essential for gardeners to plan planting and harvest schedules. Heat zones measure the number of days annually when temperatures exceed 86degF, impacting plant heat tolerance and irrigation needs. Understanding both helps optimize crop selection and planting times based on temperature extremes and seasonal climate patterns.
Mapping Your Garden: How to Find Local Frost Dates
Mapping your garden with accurate frost dates is essential for optimizing planting schedules and protecting sensitive plants. Local frost dates, which indicate the typical first and last frost of the season, vary widely depending on your USDA Hardiness Zone and Heat Zone classifications. Utilize regional frost date maps and weather databases to determine the precise freezing periods and tailor your garden care accordingly, ensuring maximal growth and seasonal success.
Decoding the Heat Zone Map for Successful Gardening
Understanding frost dates is crucial for protecting plants from cold damage, while heat zones indicate a plant's tolerance to high temperatures, guiding proper selection and care. The Heat Zone Map categorizes regions by the average number of days per year with temperatures above 86degF, helping gardeners choose plants suited to local heat stress levels. Combining frost date knowledge with heat zone information maximizes plant survival and growth throughout the growing season.
Planting Strategies: Using Frost Dates vs Heat Zones
Understanding frost dates is crucial for planting strategies, as it helps gardeners avoid damage from unexpected cold snaps by determining the last spring frost and first fall frost dates. Heat zones, defined by the average number of days above 86degF (30degC), guide plant selection based on a region's summer heat tolerance. Combining frost date data with heat zone information allows for precise timing of planting schedules and choice of crops that can thrive in both cold and hot conditions within a specific growing season.
Climate Change Impact: Shifts in Frost Dates and Heat Zones
Climate change accelerates shifts in frost dates, causing earlier last frost in spring and later first frost in fall, extending growing seasons in many regions. Heat zones are simultaneously shifting to higher temperatures, increasing plant stress and altering regional agricultural viability. These changes complicate traditional planting calendars and require adaptive strategies to mitigate crop losses and ensure food security.
Choosing Plants: Matching Frost Dates with Heat Tolerance
Selecting plants based on frost dates and heat zones ensures optimal growth by aligning species with their climatic needs. Early or late frost dates dictate planting schedules to avoid damage, while heat zone compatibility helps plants withstand temperature extremes throughout the growing season. Understanding USDA hardiness zones alongside the American Horticultural Society's heat zones enables gardeners to choose plants that match both cold tolerance and heat resilience.
Planning Your Garden Calendar: Frost Dates and Heat Zones in Sync
Frost dates mark the critical periods when temperatures drop below freezing, directly impacting planting schedules and crop survival. Heat zones classify regions based on the number of days per year with temperatures above 86degF, influencing plant heat tolerance and watering needs. Synchronizing frost dates with heat zones enables precise garden calendar planning, optimizing planting times for both cold-sensitive and heat-tolerant species.
Tools and Resources: Track Frost Dates and Heat Zones Accurately
Tracking frost dates and heat zones accurately involves utilizing specialized tools such as USDA Plant Hardiness Zone maps and local climate databases, which provide detailed temperature thresholds essential for gardening and agriculture planning. Digital applications and online platforms like the National Weather Service frost date calculator and the American Horticultural Society Heat Zone Map allow users to input geographic data to receive precise frost date predictions and heat zone classifications. Access to these tools ensures optimal planting schedules, enhances crop survival rates, and maximizes yield by aligning agricultural activities with local seasonal climate variations.
Frost dates vs Heat zones Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com