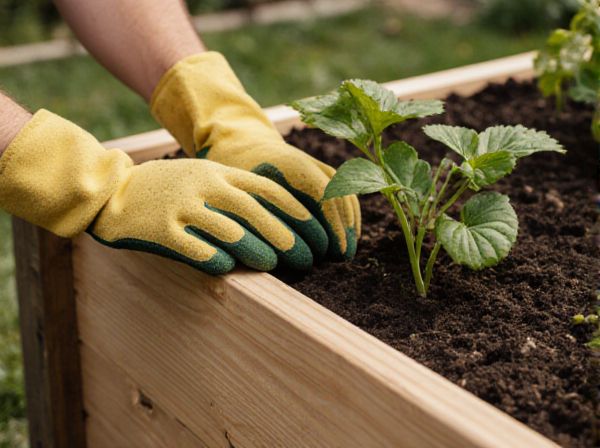

Raised bed vs Traditional ground planting Illustration
Raised beds improve soil drainage and prevent compaction, promoting healthier root development compared to traditional ground planting. They allow for better control over soil quality and reduce weed growth, enhancing overall plant productivity. Elevated soil temperatures in raised beds extend the growing season, offering advantages for early planting and faster crop maturation.
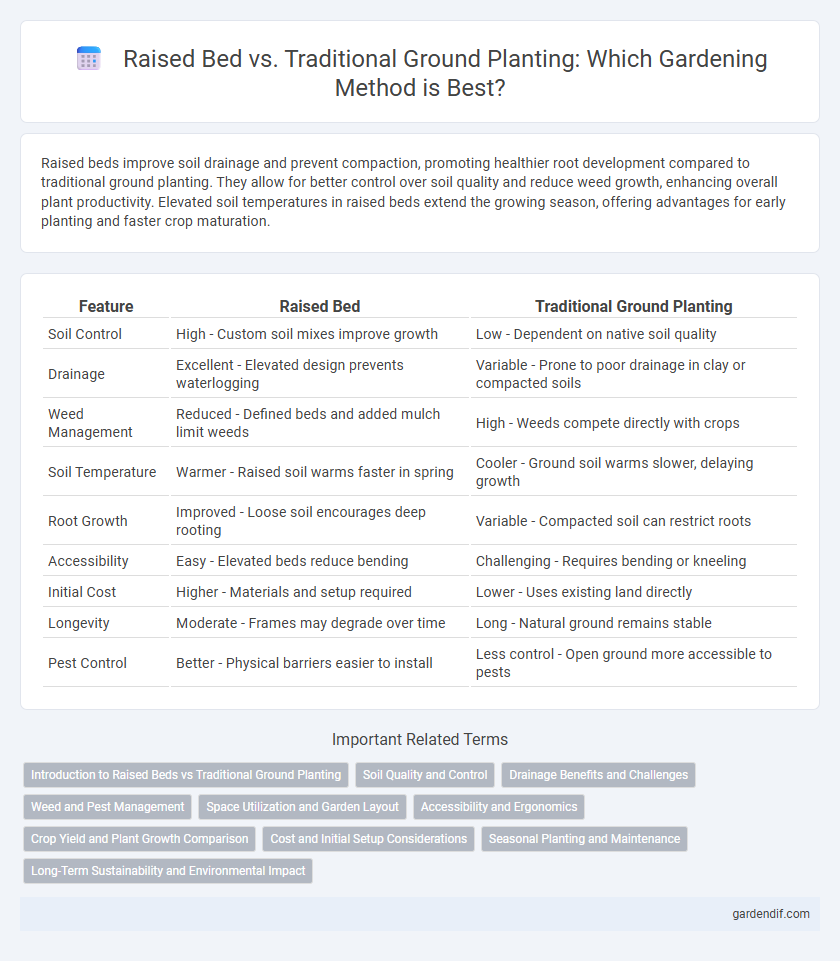
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Raised Bed | Traditional Ground Planting |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Control | High - Custom soil mixes improve growth | Low - Dependent on native soil quality |
| Drainage | Excellent - Elevated design prevents waterlogging | Variable - Prone to poor drainage in clay or compacted soils |
| Weed Management | Reduced - Defined beds and added mulch limit weeds | High - Weeds compete directly with crops |
| Soil Temperature | Warmer - Raised soil warms faster in spring | Cooler - Ground soil warms slower, delaying growth |
| Root Growth | Improved - Loose soil encourages deep rooting | Variable - Compacted soil can restrict roots |
| Accessibility | Easy - Elevated beds reduce bending | Challenging - Requires bending or kneeling |
| Initial Cost | Higher - Materials and setup required | Lower - Uses existing land directly |
| Longevity | Moderate - Frames may degrade over time | Long - Natural ground remains stable |
| Pest Control | Better - Physical barriers easier to install | Less control - Open ground more accessible to pests |
Introduction to Raised Beds vs Traditional Ground Planting
Raised beds provide superior soil drainage and improved root aeration compared to traditional ground planting, enhancing plant growth and yield. They allow precise control over soil composition and pH levels, reducing weeds and pests, which often plague in-ground gardens. Elevated soil temperatures in raised beds extend the growing season, offering an advantage over conventional ground planting methods.
Soil Quality and Control
Raised beds offer superior soil quality and control compared to traditional ground planting by allowing gardeners to customize soil composition, improve drainage, and reduce compaction. The contained environment in raised beds minimizes weed growth and soil erosion while enabling precise nutrient management tailored to specific plants. Enhanced aeration and warmth in raised beds also promote healthier root development and higher yields.
Drainage Benefits and Challenges
Raised beds offer significantly improved drainage compared to traditional ground planting by elevating soil above the natural ground level, preventing waterlogging and promoting root health. Traditional ground planting often suffers from poor drainage in heavy or compacted soils, leading to root rot and reduced plant growth. However, raised beds can dry out faster, requiring more frequent watering to maintain optimal moisture levels.
Weed and Pest Management
Raised beds improve weed and pest management by providing better soil control and drainage, reducing weed seed presence and minimizing pest habitats. The elevated structure facilitates easier access for manual weeding and targeted application of pest control measures. Compared to traditional ground planting, raised beds often experience fewer weed invasions and lower pest infestations due to enhanced airflow and soil quality management.
Space Utilization and Garden Layout
Raised beds maximize space utilization by allowing closer plant spacing and layered planting, optimizing limited garden areas more efficiently than traditional ground planting. Their defined borders and elevated structure create organized garden layouts that improve access and reduce soil compaction, resulting in healthier plant growth. Traditional ground planting often requires wider spacing to prevent competition, leading to less efficient garden use and more irregular layouts.
Accessibility and Ergonomics
Raised beds improve accessibility by elevating the planting area, reducing the need to bend or kneel, which benefits gardeners with mobility challenges or back problems. The defined edges and compact size of raised beds create ergonomic working heights that minimize strain during planting, weeding, and harvesting. Traditional ground planting often requires prolonged stooping, making raised beds a more user-friendly option for maintaining physical comfort.
Crop Yield and Plant Growth Comparison
Raised beds enhance crop yield and plant growth by improving soil drainage, aeration, and root development compared to traditional ground planting. The controlled soil environment in raised beds promotes faster nutrient uptake and reduces soil compaction, leading to healthier plants and higher productivity. Studies indicate that crops grown in raised beds can yield up to 30% more than those planted directly in the ground under similar conditions.
Cost and Initial Setup Considerations
Raised beds typically require higher initial investment due to the cost of materials such as lumber, soil, and hardware, while traditional ground planting relies primarily on existing soil and minimal supplies. The setup time for raised beds is generally longer, as it involves constructing the frame and filling it with quality soil, whereas traditional planting only requires soil preparation. Despite the upfront costs, raised beds can reduce long-term expenses by improving soil drainage and minimizing weed control efforts.
Seasonal Planting and Maintenance
Raised beds offer improved soil drainage and temperature control, enabling earlier seasonal planting and extending growing periods compared to traditional ground planting. They facilitate easier weed management and reduce soil compaction, thus lowering maintenance efforts throughout the growing season. Enhanced root aeration and nutrient control in raised beds promote healthier plant growth with less frequent intervention.
Long-Term Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Raised beds enhance long-term sustainability by improving soil structure, drainage, and nutrient retention, which reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and frequent soil amendments compared to traditional ground planting. They prevent soil erosion and compaction, promoting healthier root growth and increased biodiversity in the garden ecosystem. Raised beds also minimize water runoff and promote efficient water usage, mitigating environmental impact and supporting sustainable gardening practices over time.
Raised bed vs Traditional ground planting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com