
renewal pruning vs restorative pruning Illustration
Renewal pruning involves selectively cutting back older branches to encourage vigorous new growth, enhancing the overall health and productivity of the plant. Restorative pruning aims to revive neglected or overgrown plants by removing dead, diseased, or overcrowded stems to restore their structure and vitality. Both techniques are essential for maintaining plant longevity but serve different purposes depending on the plant's condition and desired outcome.
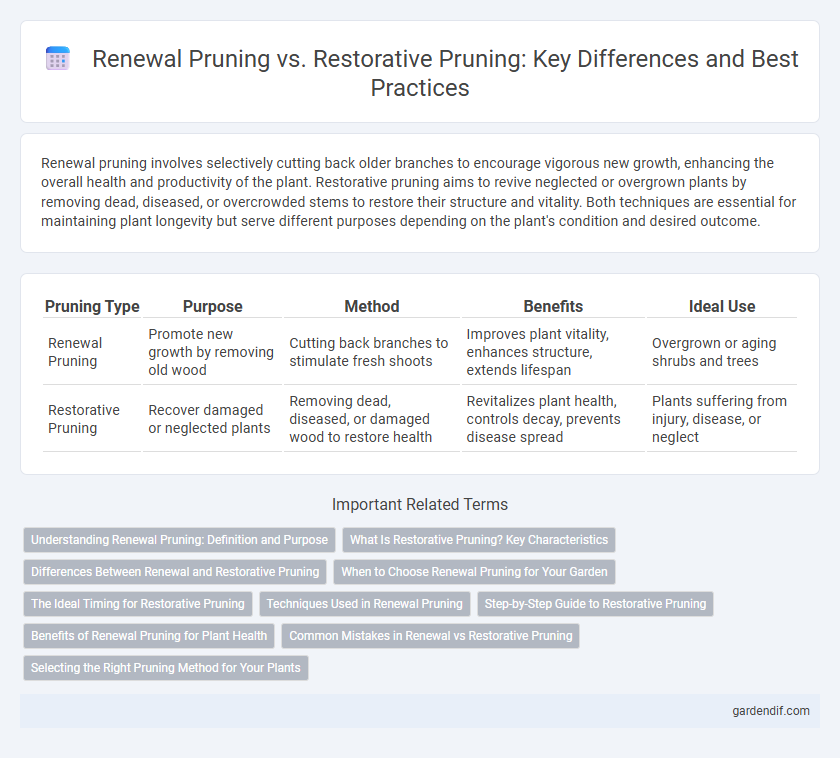
Table of Comparison
| Pruning Type | Purpose | Method | Benefits | Ideal Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renewal Pruning | Promote new growth by removing old wood | Cutting back branches to stimulate fresh shoots | Improves plant vitality, enhances structure, extends lifespan | Overgrown or aging shrubs and trees |
| Restorative Pruning | Recover damaged or neglected plants | Removing dead, diseased, or damaged wood to restore health | Revitalizes plant health, controls decay, prevents disease spread | Plants suffering from injury, disease, or neglect |
Understanding Renewal Pruning: Definition and Purpose
Renewal pruning involves selectively removing older branches to stimulate the growth of new shoots, enhancing the overall vitality and productivity of a plant. This method focuses on rejuvenating mature trees or shrubs by encouraging fresh, healthy growth that improves structure and fruiting potential. Renewal pruning is particularly effective in managing plant age and optimizing long-term health and yield.
What Is Restorative Pruning? Key Characteristics
Restorative pruning involves selectively removing damaged, diseased, or overgrown branches to enhance the health and structure of mature trees or plants. Key characteristics include targeting structural defects, improving airflow and light penetration, and encouraging natural growth patterns without causing significant stress. This method contrasts with renewal pruning, which focuses primarily on stimulating new growth through more aggressive cutting.
Differences Between Renewal and Restorative Pruning
Renewal pruning targets older branches to stimulate new growth and improve overall tree vitality, typically removing one-third of the plant each season. Restorative pruning focuses on repairing damaged or overgrown trees by strategically cutting back to sound wood or healthy branches to restore structural integrity. The key difference lies in renewal pruning promoting ongoing growth cycles, while restorative pruning aims at recovery and improving existing tree structure.
When to Choose Renewal Pruning for Your Garden
Renewal pruning is ideal when plants show signs of age-related decline, such as reduced flowering or sparse foliage, as it stimulates vigorous new growth by cutting back old wood. This method is best applied during the dormant season to encourage healthy regeneration without stressing the plant. Choose renewal pruning for overgrown shrubs or perennials needing rejuvenation to restore their shape and productivity efficiently.
The Ideal Timing for Restorative Pruning
Restorative pruning is ideally performed during late winter or early spring when trees are still dormant, minimizing stress and reducing the risk of disease. This timing allows for optimal wound closure and promotes vigorous new growth in the upcoming growing season. Pruning during this period also helps maintain structural integrity and enhances the tree's long-term health and resilience.
Techniques Used in Renewal Pruning
Renewal pruning techniques primarily involve selectively removing older, less productive branches to stimulate new growth and improve overall plant health. This method includes thinning out crowded areas, cutting back to healthy buds or stems, and ensuring adequate light penetration to encourage vigorous shoot development. By applying these targeted cuts, renewal pruning maximizes fruit yield and extends the productive lifespan of orchard trees or shrubs.
Step-by-Step Guide to Restorative Pruning
Restorative pruning involves methodically removing dead, diseased, or overgrown branches to revive tree health and structure, starting with identifying hazardous limbs and making clean cuts at branch collars. This process includes thinning dense areas to improve light penetration and air circulation, promoting vigorous new growth. Final steps focus on shaping the canopy to restore its natural form while minimizing stress and preventing further damage.
Benefits of Renewal Pruning for Plant Health
Renewal pruning stimulates vigorous new growth by removing old, unproductive branches, enhancing overall plant vitality. It improves air circulation and sunlight penetration, reducing the risk of fungal diseases and pest infestations. This method promotes a stronger structure and prolonged lifespan, ensuring sustainable plant health and productivity.
Common Mistakes in Renewal vs Restorative Pruning
Common mistakes in renewal pruning include removing too much live wood, which weakens the tree's structure and reduces fruit production, whereas restorative pruning errors often involve neglecting the tree's natural growth patterns, leading to distorted shapes and reduced vigor. Both practices require understanding the tree species' growth cycle to avoid over-pruning or uneven cuts that cause stress and disease susceptibility. Proper timing and selective cutting are essential to optimize recovery and maintain long-term tree health.
Selecting the Right Pruning Method for Your Plants
Selecting the right pruning method depends on the plant's health and growth goals; renewal pruning targets older branches to stimulate vigorous new growth, while restorative pruning focuses on rehabilitating damaged or neglected plants by removing dead or overgrown limbs. Understanding plant species-specific growth patterns and seasonal timing enhances the effectiveness of renewal and restorative pruning techniques. Optimal pruning practices improve plant structure, promote disease resistance, and maximize flowering or fruiting potential.
renewal pruning vs restorative pruning Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com