
Renewal pruning vs reduction pruning Illustration
Renewal pruning involves selectively removing older branches to stimulate new growth and improve overall plant health. Reduction pruning, on the other hand, shortens branches to decrease their size while maintaining the plant's natural shape. Both techniques enhance plant vitality but serve different purposes in managing growth and structure.
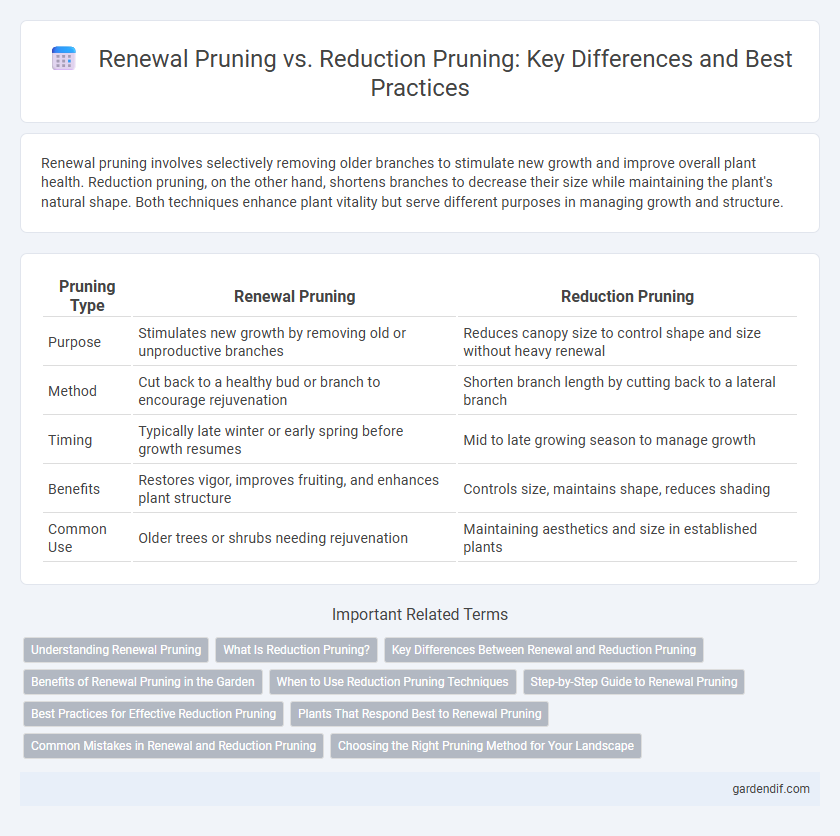
Table of Comparison
| Pruning Type | Renewal Pruning | Reduction Pruning |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Stimulates new growth by removing old or unproductive branches | Reduces canopy size to control shape and size without heavy renewal |
| Method | Cut back to a healthy bud or branch to encourage rejuvenation | Shorten branch length by cutting back to a lateral branch |
| Timing | Typically late winter or early spring before growth resumes | Mid to late growing season to manage growth |
| Benefits | Restores vigor, improves fruiting, and enhances plant structure | Controls size, maintains shape, reduces shading |
| Common Use | Older trees or shrubs needing rejuvenation | Maintaining aesthetics and size in established plants |
Understanding Renewal Pruning
Renewal pruning focuses on stimulating vigorous new growth by selectively removing older, less productive branches to rejuvenate the plant's structure. This technique enhances plant health and productivity by encouraging stronger shoots and improving air circulation. Understanding the principles of renewal pruning ensures the long-term vitality and balanced development of trees and shrubs.
What Is Reduction Pruning?
Reduction pruning involves selectively cutting back branches to decrease the overall size and canopy density of a tree, enhancing structural integrity and light penetration. Unlike renewal pruning, which focuses on stimulating new growth by removing older wood, reduction pruning reshapes mature trees to manage height and spread, preventing hazards and improving aesthetic form. This method is essential in maintaining tree health in urban and residential landscapes by minimizing stress and decay risks associated with excessive growth.
Key Differences Between Renewal and Reduction Pruning
Renewal pruning involves selectively removing older branches to stimulate new growth, enhancing the overall health and productivity of the plant. Reduction pruning focuses on shortening the length of branches to reduce size without drastically altering the plant's shape or stimulating new shoots. Key differences include the purpose: renewal pruning encourages regeneration by cutting older wood, while reduction pruning manages size and shape by trimming back branch tips.
Benefits of Renewal Pruning in the Garden
Renewal pruning enhances garden vitality by stimulating new growth and improving air circulation, which reduces disease risks. This method encourages the development of strong, productive branches, leading to increased flowering and fruiting potential. Pruning for renewal also helps maintain the plant's structure, promoting long-term health and aesthetic appeal.
When to Use Reduction Pruning Techniques
Reduction pruning techniques are essential when managing tree size, controlling growth, and minimizing risk in urban landscapes or confined spaces where height and spread must be limited. These methods are ideal for older or overgrown trees requiring structural correction without stimulating excessive new growth. Implement reduction pruning to maintain tree health and safety while preserving natural form, especially when clearance for buildings, power lines, or traffic is needed.
Step-by-Step Guide to Renewal Pruning
Renewal pruning involves systematically removing older branches to stimulate new growth and maintain tree vigor, typically targeting one-third of the oldest wood each season to avoid stress. Begin by identifying and marking the oldest or weakest branches, then carefully cut them back to a strong lateral branch or bud to encourage healthy shoots. Follow up with thinning cuts that improve air circulation and light penetration, ensuring the tree's structure remains balanced for sustained health and productivity.
Best Practices for Effective Reduction Pruning
Effective reduction pruning involves selectively shortening branches to maintain the tree's natural shape while improving light penetration and air circulation. Best practices include cutting back to a lateral branch that is at least one-third the diameter of the parent branch and avoiding topping, which can lead to weak regrowth and decay. Proper timing during the dormant season minimizes stress, promoting healthy regrowth and long-term tree vitality.
Plants That Respond Best to Renewal Pruning
Plants that respond best to renewal pruning include many deciduous shrubs such as lilacs, forsythia, and elderberry, which benefit from having older wood removed to stimulate vigorous new growth. Renewal pruning works effectively on species with strong regenerative capabilities, like butterfly bush (Buddleja) and certain viburnums, promoting fuller, healthier plants with enhanced flowering. This method contrasts with reduction pruning, which targets size control whereas renewal pruning focuses on rejuvenating plant health and vitality.
Common Mistakes in Renewal and Reduction Pruning
Common mistakes in renewal pruning include cutting too close to the main branch, which hampers new growth, and removing too many old branches at once, leading to stress on the plant. In reduction pruning, improper cuts often occur by not selecting appropriate lateral branches to maintain the plant's natural shape, resulting in an imbalanced appearance and poor regrowth. Both methods can cause damage if pruning tools are unclean or cuts are ragged, increasing the risk of disease and decay.
Choosing the Right Pruning Method for Your Landscape
Renewal pruning focuses on revitalizing mature plants by removing old, overgrown branches to stimulate new growth, ideal for restoring plant health and vigor. Reduction pruning involves selectively shortening branch length to control size and shape without drastically altering the plant's structure, making it suitable for maintaining spatial constraints in urban landscapes. Selecting the appropriate method depends on the plant species, age, desired aesthetic outcome, and overall landscape goals to ensure optimal growth and visual appeal.
Renewal pruning vs reduction pruning Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com