
Formative pruning vs corrective pruning Illustration
Formative pruning shapes young plants to establish strong structure and promote healthy growth, preventing future problems. Corrective pruning addresses issues in mature plants by removing damaged or diseased branches and improving overall appearance. Both techniques are essential for maintaining plant health and maximizing lifespan.
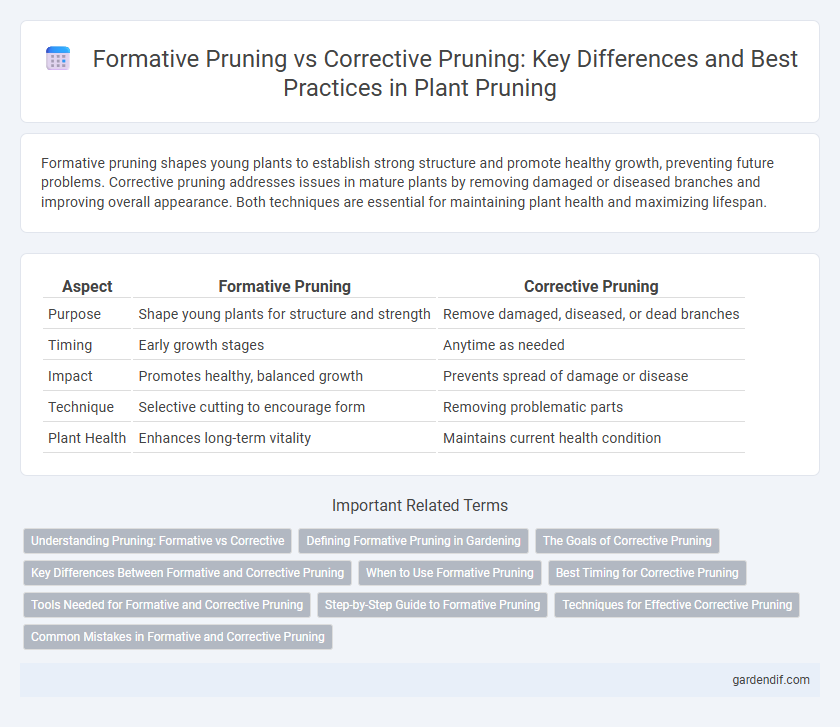
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Formative Pruning | Corrective Pruning |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Shape young plants for structure and strength | Remove damaged, diseased, or dead branches |
| Timing | Early growth stages | Anytime as needed |
| Impact | Promotes healthy, balanced growth | Prevents spread of damage or disease |
| Technique | Selective cutting to encourage form | Removing problematic parts |
| Plant Health | Enhances long-term vitality | Maintains current health condition |
Understanding Pruning: Formative vs Corrective
Formative pruning shapes young plants by selectively removing branches to develop a strong structure, promoting healthy growth and optimal light exposure. Corrective pruning targets mature plants to fix issues like damaged, diseased, or overcrowded branches, enhancing plant health and productivity. Understanding the distinct timing and objectives of formative versus corrective pruning is essential for effective horticultural management.
Defining Formative Pruning in Gardening
Formative pruning shapes young plants to establish a strong structure, improving future growth and productivity. This method involves selectively removing specific branches during the early stages of development to enhance the plant's natural form and balance. In gardening, formative pruning lays the foundation for healthy, well-structured trees and shrubs by guiding growth patterns and preventing structural issues.
The Goals of Corrective Pruning
Corrective pruning aims to restore tree health by removing damaged, diseased, or dead branches to prevent decay and pest infestations. It focuses on improving structural integrity and safety while enhancing the tree's appearance after storm damage or improper growth patterns. This type of pruning supports the long-term vitality of the tree by minimizing stress and encouraging balanced growth.
Key Differences Between Formative and Corrective Pruning
Formative pruning shapes young plants to establish a strong structure and promote desired growth patterns, primarily conducted during the plant's early stages. Corrective pruning removes damaged, diseased, or poorly positioned branches to maintain plant health and improve appearance in mature plants. The key differences lie in their timing, purpose, and impact on plant development, with formative pruning focusing on long-term structural goals and corrective pruning addressing immediate health and aesthetic issues.
When to Use Formative Pruning
Formative pruning is most effective during the early stages of a plant's growth to shape its structure and promote healthy development. This method guides the formation of strong branches, optimizing light penetration and air circulation, which reduces disease risks. Employ formative pruning in the first few years after planting to establish a durable framework and prevent future corrective issues.
Best Timing for Corrective Pruning
Effective corrective pruning is best performed during late winter or early spring before new growth begins, ensuring minimal stress to the tree and promoting healthy recovery. This timing supports the plant's natural healing processes and reduces the risk of disease infection after cuts are made. Pruning during dormancy maximizes energy allocation for branch regrowth and structural correction.
Tools Needed for Formative and Corrective Pruning
Formative pruning typically requires hand pruners, loppers, and sometimes a pruning saw to precisely shape young plants and encourage strong structural growth. Corrective pruning often involves more robust tools such as pole pruners and heavy-duty saws to remove larger, damaged, or overgrown branches in mature trees. Both pruning types benefit from sharp, clean cutting tools to promote healthy healing and minimize plant stress.
Step-by-Step Guide to Formative Pruning
Formative pruning involves strategically removing specific branches during the early growth stages of a plant to establish a strong framework and promote healthy development. Start by identifying and cutting weak, crossing, or inward-growing branches to improve air circulation and light penetration. Regularly monitor and adjust the structure by making precise cuts that encourage balanced growth and shape the plant for optimal strength and productivity.
Techniques for Effective Corrective Pruning
Effective corrective pruning techniques include selective branch removal to eliminate damaged, diseased, or crossing limbs, promoting tree health and structure. Pruners use thinning cuts to improve light penetration and air circulation, reducing the risk of pest infestation and disease. Precise timing and proper pruning tools are essential to minimize stress and encourage vigorous regrowth in corrective pruning practices.
Common Mistakes in Formative and Corrective Pruning
Common mistakes in formative pruning include removing too much growth early, which weakens the tree's structure and reduces future vigor, and improper selection of scaffold branches that can lead to poor canopy shape and reduced stability. In corrective pruning, frequent errors involve cutting large branches incorrectly, causing decay or excessive wound exposure, and neglecting to address crossing or rubbing branches, which promotes disease and structural weakness. Both pruning types require precise cuts and timing to maintain tree health and optimize growth patterns.
Formative pruning vs corrective pruning Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com