
Trap Cropping vs Mass Trapping Illustration
Trap cropping involves planting specific crops that attract pests away from the main crop, effectively reducing damage by concentrating pests in a controlled area. Mass trapping uses large numbers of traps to capture and remove pests from the environment, decreasing their population across the entire field. Both methods aim to minimize chemical pesticide use by managing pest behavior through targeted interventions.
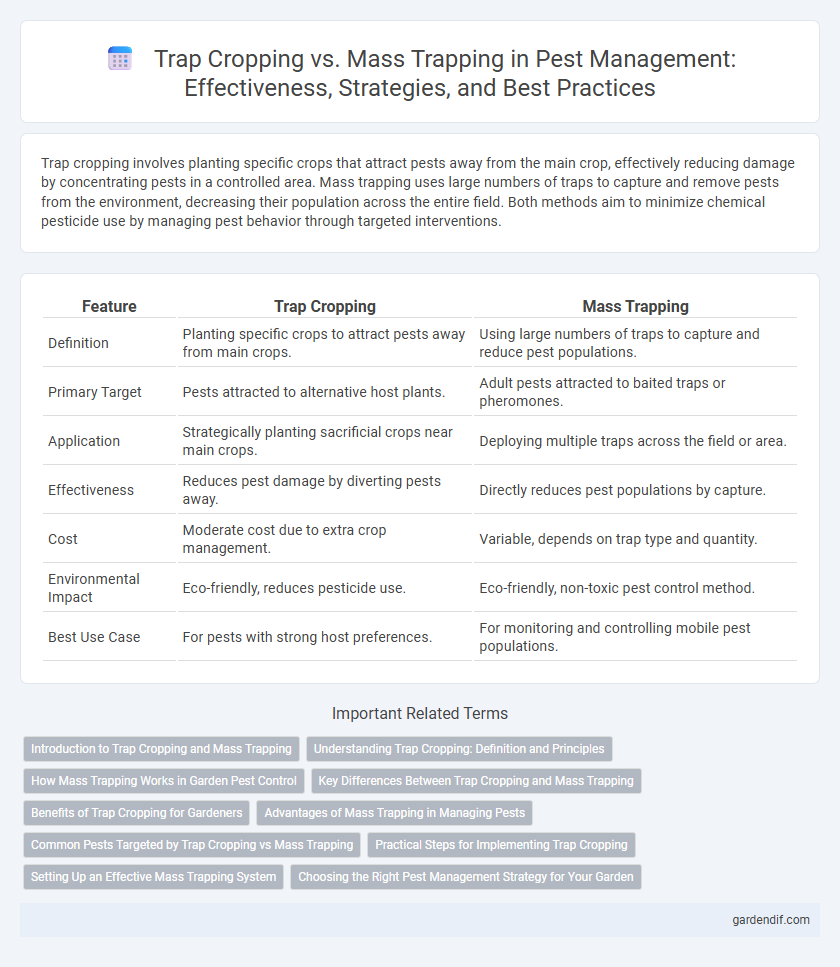
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Trap Cropping | Mass Trapping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Planting specific crops to attract pests away from main crops. | Using large numbers of traps to capture and reduce pest populations. |
| Primary Target | Pests attracted to alternative host plants. | Adult pests attracted to baited traps or pheromones. |
| Application | Strategically planting sacrificial crops near main crops. | Deploying multiple traps across the field or area. |
| Effectiveness | Reduces pest damage by diverting pests away. | Directly reduces pest populations by capture. |
| Cost | Moderate cost due to extra crop management. | Variable, depends on trap type and quantity. |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, reduces pesticide use. | Eco-friendly, non-toxic pest control method. |
| Best Use Case | For pests with strong host preferences. | For monitoring and controlling mobile pest populations. |
Introduction to Trap Cropping and Mass Trapping
Trap cropping involves planting specific crops to attract pests away from the main crop, reducing damage and minimizing pesticide use. Mass trapping employs large numbers of traps targeting pest populations directly to suppress their numbers effectively. Both strategies serve as integral components of integrated pest management by leveraging pest behavior for sustainable control.
Understanding Trap Cropping: Definition and Principles
Trap cropping involves planting specific crops to attract pests away from the main crop, effectively reducing damage and improving pest management. This method relies on pest behavior and preferences, using sacrificial plants as a decoy to divert harmful insects. Understanding the principles of trap cropping helps optimize its implementation, enhancing crop protection and minimizing pesticide use.
How Mass Trapping Works in Garden Pest Control
Mass trapping controls garden pests by deploying a large number of specialized traps to capture and reduce pest populations before they cause significant damage. This method targets specific insect species such as fruit flies, aphids, and whiteflies using pheromone or food-based lures that attract pests en masse. By lowering the overall pest density, mass trapping minimizes the need for chemical pesticides and promotes sustainable pest management in gardens.
Key Differences Between Trap Cropping and Mass Trapping
Trap cropping involves planting specific crops to attract pests away from the main crop, creating a targeted pest management strategy. Mass trapping uses a large number of traps distributed throughout the field to capture and reduce pest populations broadly. The key difference lies in trap cropping's reliance on pest attraction to sacrificial plants, while mass trapping focuses on extensive physical removal of pests.
Benefits of Trap Cropping for Gardeners
Trap cropping provides gardeners with an environmentally friendly method to protect their plants by attracting pests away from main crops, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. This technique enhances pest management by concentrating harmful insects on specific plants, making it easier to monitor and control infestations. Gardeners benefit from improved crop health, higher yields, and biodiversity preservation within their gardens.
Advantages of Mass Trapping in Managing Pests
Mass trapping effectively reduces pest populations by using a high density of traps to capture large numbers of insects, minimizing crop damage without relying on chemical pesticides. This method targets specific pest species, enhancing control precision and reducing harm to beneficial insects and the environment. Mass trapping also allows continuous monitoring of pest abundance, enabling timely and informed pest management decisions.
Common Pests Targeted by Trap Cropping vs Mass Trapping
Trap cropping targets specific pests such as aphids, whiteflies, and cucumber beetles by using preferred plants to lure them away from crops, effectively reducing localized infestations. Mass trapping focuses on a broader spectrum of pests including fruit flies, codling moths, and thrips, utilizing large numbers of traps to capture and significantly lower pest populations across agricultural areas. Both strategies optimize pest management by exploiting pest behavior but differ in scale and target specificity.
Practical Steps for Implementing Trap Cropping
Trap cropping involves planting a preferred pest-attracting crop near the main crop to divert pests and reduce infestations, requiring careful selection of trap crop species based on pest preferences. Effective trap cropping requires timely planting of trap crops ahead of the main crop, monitoring pest populations regularly, and integrating targeted pest control measures on trap plants to prevent pest overflow. Proper spatial arrangement and maintaining trap crops' health are critical to enhancing pest capture and protecting the primary crop sustainably.
Setting Up an Effective Mass Trapping System
Setting up an effective mass trapping system requires selecting highly attractive trap crops or pheromone traps that target specific pest species, ensuring high capture rates. Placement density and spatial arrangement are critical, with traps positioned uniformly around the main crop at recommended intervals to maximize pest interception and reduce population pressure. Regular monitoring and maintenance, including trap replacement and lure refreshment, sustain trap efficacy throughout the growing season.
Choosing the Right Pest Management Strategy for Your Garden
Trap cropping involves planting specific crops that attract pests away from the main garden, effectively reducing pest pressure on valuable plants. Mass trapping uses numerous traps to capture and reduce pest populations directly, proving beneficial for large infestations. Choosing the right pest management strategy depends on pest species, garden size, and crop value, ensuring targeted, eco-friendly control.
Trap Cropping vs Mass Trapping Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com