
Hand picking vs biological control Illustration
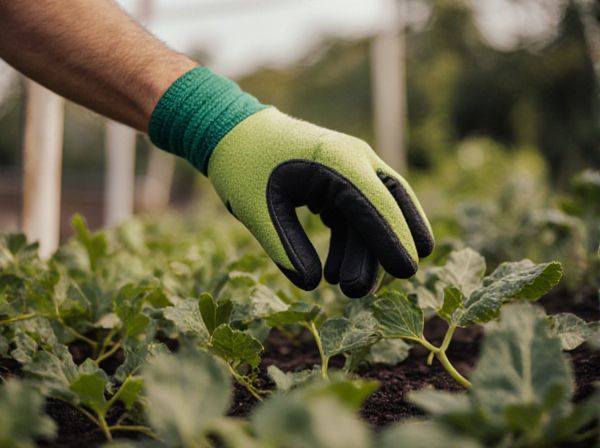
Hand picking pests is a labor-intensive method that allows for the immediate removal of visible insects, minimizing chemical use and preserving beneficial organisms. Biological control employs natural predators or parasites to maintain pest populations at manageable levels, promoting long-term ecological balance. Combining these strategies can effectively reduce pest damage while supporting sustainable agricultural practices.
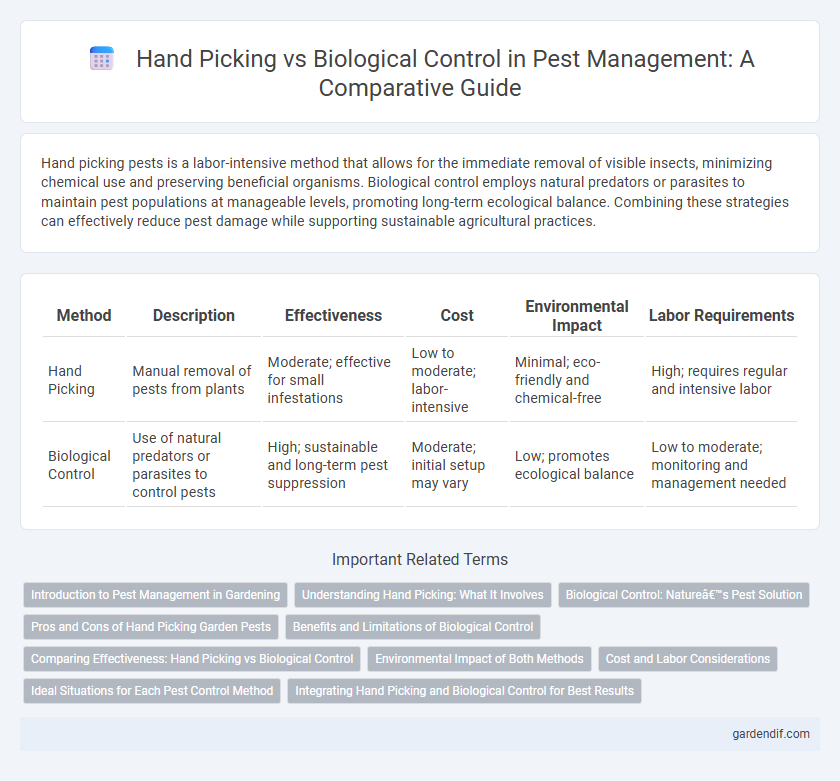
Table of Comparison
| Method | Description | Effectiveness | Cost | Environmental Impact | Labor Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hand Picking | Manual removal of pests from plants | Moderate; effective for small infestations | Low to moderate; labor-intensive | Minimal; eco-friendly and chemical-free | High; requires regular and intensive labor |
| Biological Control | Use of natural predators or parasites to control pests | High; sustainable and long-term pest suppression | Moderate; initial setup may vary | Low; promotes ecological balance | Low to moderate; monitoring and management needed |
Introduction to Pest Management in Gardening
Hand picking offers a direct, chemical-free method to eliminate pests by manually removing insects like aphids, caterpillars, and beetles from plants, promoting immediate pest reduction in small-scale gardening. Biological control utilizes natural predators such as ladybugs, parasitic wasps, and nematodes to maintain pest populations below damaging levels, enhancing garden biodiversity and minimizing pesticide use. Combining hand picking with biological control strategies supports integrated pest management (IPM), optimizing sustainable and eco-friendly pest suppression in diverse garden ecosystems.
Understanding Hand Picking: What It Involves
Hand picking involves manually removing pests from plants, which provides targeted control without the use of chemicals, making it an eco-friendly pest management method. This technique is particularly effective for managing small infestations of insects like caterpillars, beetles, and aphids in home gardens or small-scale farms. Understanding the specific pest's behavior and habitat is crucial for efficiently implementing hand picking as part of an integrated pest management strategy.
Biological Control: Nature’s Pest Solution
Biological control exploits natural predators, parasites, or pathogens to manage pest populations sustainably, reducing reliance on chemical pesticides. Beneficial organisms like ladybugs, parasitic wasps, and entomopathogenic fungi target specific pests, promoting ecosystem balance and minimizing environmental impact. This method enhances long-term pest suppression by fostering biodiversity and resilience within agricultural and natural systems.
Pros and Cons of Hand Picking Garden Pests
Hand picking garden pests offers the advantage of immediate removal without chemical use, making it environmentally friendly and safe for beneficial insects. However, it is labor-intensive and impractical for large infestations or fast-reproducing pests. This method allows precise control but may require frequent monitoring to effectively manage pest populations.
Benefits and Limitations of Biological Control
Biological control offers sustainable pest management by using natural predators or parasites to reduce pest populations, minimizing chemical pesticide use and environmental impact. It supports long-term pest suppression and enhances biodiversity but may be slower to achieve control and less effective against pests with high reproductive rates. Limitations include the risk of non-target effects and the need for careful species selection and monitoring to ensure ecological balance.
Comparing Effectiveness: Hand Picking vs Biological Control
Hand picking targets individual pests, offering immediate and precise removal but can be labor-intensive and less feasible for large infestations. Biological control employs natural predators or parasites, providing sustainable, long-term pest population suppression with minimal environmental impact. Effectiveness varies with pest type and infestation scale, often making biological control more suitable for widespread or recurring pest issues.
Environmental Impact of Both Methods
Hand picking pests minimizes chemical use and preserves surrounding biodiversity, offering an eco-friendly pest control alternative with low environmental impact. Biological control relies on natural predators or parasites, reducing pesticide dependence but requires careful species selection to prevent ecosystem imbalance. Both methods promote sustainable agriculture by lowering chemical residue and supporting soil health compared to conventional pesticide use.
Cost and Labor Considerations
Hand picking pests requires significant manual labor and can become costly over large areas, making it less practical for extensive infestations. Biological control involves using natural predators or parasites, which may have higher initial setup costs but reduces ongoing labor expenses and offers sustainable pest management. Choosing between these methods depends on balancing immediate labor costs with long-term financial and environmental benefits.
Ideal Situations for Each Pest Control Method
Hand picking is ideal for small-scale infestations where pests like caterpillars or beetles are visible and accessible, offering immediate removal without chemicals. Biological control suits larger or more complex ecosystems, effectively managing pest populations such as aphids or whiteflies through natural predators like ladybugs or parasitic wasps. Selecting the appropriate method depends on infestation size, pest type, and environmental conditions to ensure sustainable and targeted pest management.
Integrating Hand Picking and Biological Control for Best Results
Integrating hand picking and biological control enhances pest management efficiency by combining immediate removal of pests with long-term population suppression through natural predators. Hand picking delivers precise control over larger pest infestations, while biological agents, such as predatory beetles and parasitic wasps, sustain ongoing pest reduction without chemical intervention. This combined strategy minimizes crop damage and promotes ecological balance, optimizing pest control outcomes in sustainable agriculture.
Hand picking vs biological control Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com