
Natural Pest Control vs Chemical Pest Control Illustration
Natural pest control utilizes beneficial insects, companion planting, and organic practices to maintain ecosystem balance and reduce harmful pest populations without toxic residues. Chemical pest control relies on synthetic pesticides that can provide immediate results but often harm beneficial organisms, pollute soil and water, and lead to pest resistance. Permaculture emphasizes natural methods to create sustainable, resilient gardens that support biodiversity and long-term soil health.
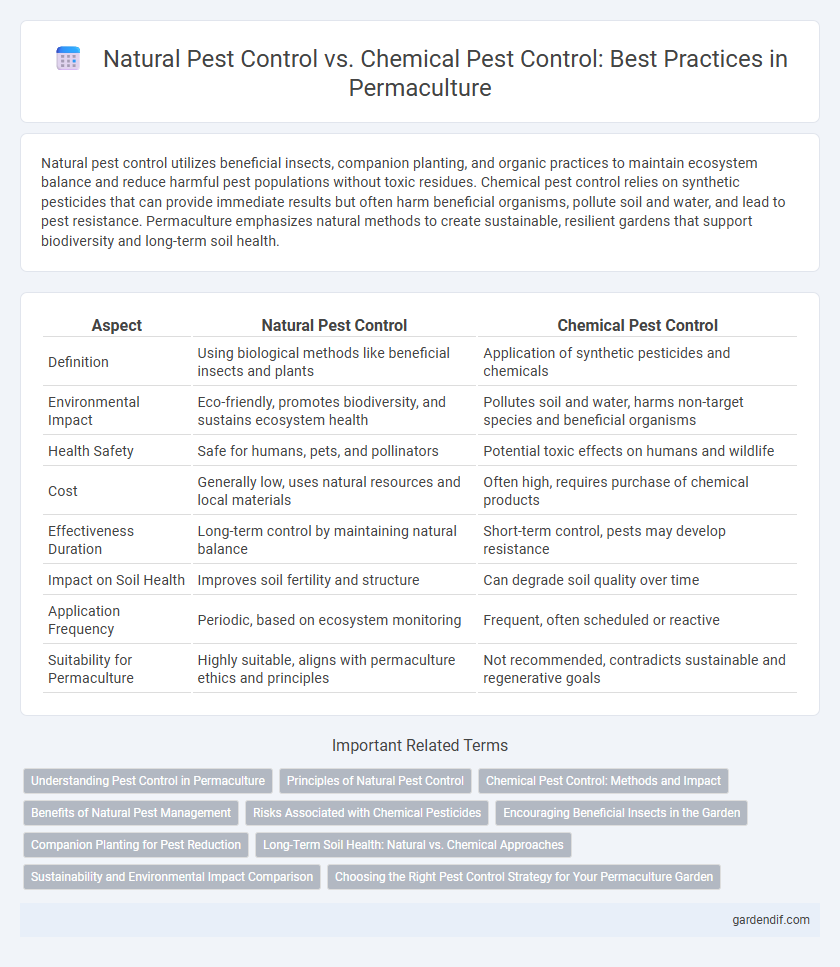
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Natural Pest Control | Chemical Pest Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Using biological methods like beneficial insects and plants | Application of synthetic pesticides and chemicals |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, promotes biodiversity, and sustains ecosystem health | Pollutes soil and water, harms non-target species and beneficial organisms |
| Health Safety | Safe for humans, pets, and pollinators | Potential toxic effects on humans and wildlife |
| Cost | Generally low, uses natural resources and local materials | Often high, requires purchase of chemical products |
| Effectiveness Duration | Long-term control by maintaining natural balance | Short-term control, pests may develop resistance |
| Impact on Soil Health | Improves soil fertility and structure | Can degrade soil quality over time |
| Application Frequency | Periodic, based on ecosystem monitoring | Frequent, often scheduled or reactive |
| Suitability for Permaculture | Highly suitable, aligns with permaculture ethics and principles | Not recommended, contradicts sustainable and regenerative goals |
Understanding Pest Control in Permaculture
Natural pest control in permaculture relies on ecosystem balance, using beneficial insects, companion planting, and organic methods to manage pests sustainably. Chemical pest control disrupts soil health, beneficial organisms, and long-term garden productivity, often leading to pest resistance and environmental harm. Emphasizing natural pest management aligns with permaculture principles by fostering biodiversity and maintaining self-regulating, resilient agricultural systems.
Principles of Natural Pest Control
Natural pest control relies on ecological balance by encouraging natural predators, promoting biodiversity, and using plant-based deterrents to manage pests effectively in permaculture systems. This method minimizes harmful chemical inputs, preserving soil health and enhancing overall ecosystem resilience. Integrating companion planting and habitat creation supports beneficial insects, which naturally suppress pest populations and reduce the need for synthetic pesticides.
Chemical Pest Control: Methods and Impact
Chemical pest control employs synthetic pesticides such as insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides to eliminate pests rapidly, but often results in environmental contamination and resistance development among target species. Persistent chemical residues can harm beneficial insects, pollinators, and soil microorganisms, disrupting ecosystem balance and reducing biodiversity in agricultural landscapes. The extensive use of chemical controls contributes to soil degradation, water pollution, and potential health risks for humans, undermining long-term sustainability goals central to permaculture principles.
Benefits of Natural Pest Management
Natural pest management in permaculture enhances biodiversity by encouraging beneficial insects and predators that naturally suppress pest populations. This approach reduces chemical residues in soil and water, promoting healthier ecosystems and safer food production. Long-term soil fertility and plant resilience improve as natural pest control methods maintain ecological balance without harmful synthetic inputs.
Risks Associated with Chemical Pesticides
Chemical pesticides pose significant risks including environmental contamination, harm to non-target species such as pollinators and beneficial insects, and the development of pesticide-resistant pest populations. These hazardous chemicals can infiltrate soil, waterways, and food chains, resulting in long-term ecological damage and potential health issues for humans and wildlife. Natural pest control methods in permaculture emphasize ecosystem balance and biodiversity, reducing reliance on synthetic toxins and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Encouraging Beneficial Insects in the Garden
Encouraging beneficial insects such as ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps enhances natural pest control by maintaining ecological balance and reducing the need for chemical pesticides. These predatory insects target harmful pests like aphids and caterpillars, promoting healthier plant growth and biodiversity in permaculture gardens. Integrating insect-attracting plants like marigolds, dill, and fennel supports a sustainable pest management strategy that aligns with permaculture principles.
Companion Planting for Pest Reduction
Companion planting is a key strategy in natural pest control within permaculture, using specific plant combinations to deter harmful insects and attract beneficial predators. Plants like marigolds, nasturtiums, and basil release natural chemicals that repel pests such as aphids, whiteflies, and nematodes, reducing the need for synthetic pesticides. This approach enhances biodiversity and soil health, creating a self-sustaining ecosystem that minimizes chemical pesticide dependency and promotes long-term pest management.
Long-Term Soil Health: Natural vs. Chemical Approaches
Natural pest control methods enhance long-term soil health by promoting beneficial microbial activity and maintaining organic matter, which supports sustainable nutrient cycling and soil structure. Chemical pest control often disrupts soil microbial communities, leading to decreased fertility, increased resistance, and potential contamination of soil and water resources. Permaculture practices favor natural approaches for their ability to preserve soil vitality, improve biodiversity, and support resilient ecosystems.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact Comparison
Natural pest control in permaculture leverages biological agents and ecosystem balance, significantly reducing chemical runoff and preserving soil health. Chemical pest control often leads to biodiversity loss and soil degradation due to toxic residues and non-target species harm. Sustainable permaculture practices prioritize natural methods to enhance resilience and long-term environmental stability.
Choosing the Right Pest Control Strategy for Your Permaculture Garden
Selecting the ideal pest control strategy for a permaculture garden hinges on prioritizing ecological balance and soil health, with natural pest control methods such as introducing beneficial insects, companion planting, and using organic sprays effectively reducing pest populations without harming the environment. Chemical pest control, while sometimes offering rapid results, often disrupts beneficial insect communities and leads to soil degradation, undermining long-term garden sustainability. Emphasizing integrated pest management (IPM) tailored to the specific ecosystem of your permaculture garden ensures both pest suppression and the preservation of biodiversity.
Natural Pest Control vs Chemical Pest Control Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com