
Greywater Recycling vs Freshwater Irrigation Illustration
Greywater recycling conserves freshwater by reusing wastewater from baths, sinks, and laundry to irrigate gardens, reducing demand on natural water sources. Freshwater irrigation often relies on treated or groundwater, which can deplete resources and increase environmental stress. Integrating greywater systems in permaculture enhances sustainability by closing the water loop and promoting efficient water use in landscaping and crop cultivation.
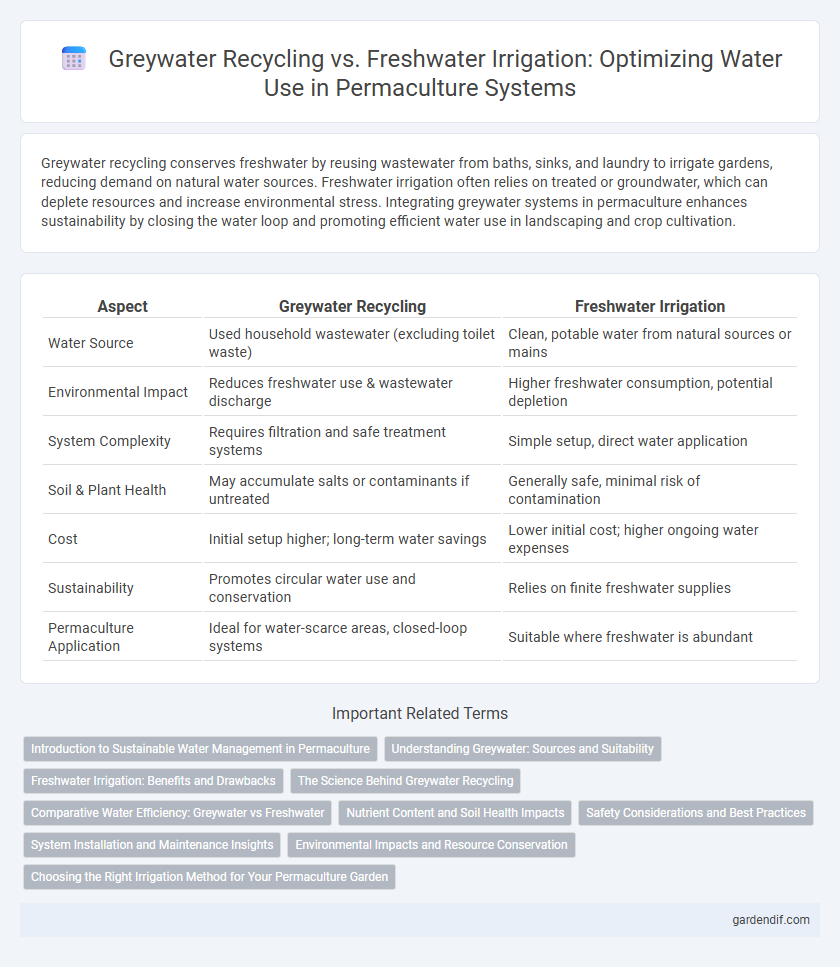
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Greywater Recycling | Freshwater Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Water Source | Used household wastewater (excluding toilet waste) | Clean, potable water from natural sources or mains |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces freshwater use & wastewater discharge | Higher freshwater consumption, potential depletion |
| System Complexity | Requires filtration and safe treatment systems | Simple setup, direct water application |
| Soil & Plant Health | May accumulate salts or contaminants if untreated | Generally safe, minimal risk of contamination |
| Cost | Initial setup higher; long-term water savings | Lower initial cost; higher ongoing water expenses |
| Sustainability | Promotes circular water use and conservation | Relies on finite freshwater supplies |
| Permaculture Application | Ideal for water-scarce areas, closed-loop systems | Suitable where freshwater is abundant |
Introduction to Sustainable Water Management in Permaculture
Greywater recycling in permaculture involves repurposing lightly used household water from sinks, showers, and laundry for irrigation, reducing freshwater demand and promoting water conservation. Freshwater irrigation relies on clean water sources, which can strain natural reserves if overused, making sustainable management crucial. Integrating greywater systems supports ecological balance by minimizing wastewater discharge and enhancing soil moisture for resilient plant growth.
Understanding Greywater: Sources and Suitability
Greywater, originating from household activities such as laundry, bathing, and dishwashing, offers a valuable resource for sustainable irrigation in permaculture systems. Its relatively low contaminant levels make it suitable for non-edible plants, reducing freshwater demand and conserving vital water resources. Proper treatment and understanding of source water characteristics ensure safe reuse, minimizing risks of harmful pathogens and chemical buildup in soil ecosystems.
Freshwater Irrigation: Benefits and Drawbacks
Freshwater irrigation provides plants with consistent access to clean water, promoting healthy growth and higher crop yields in permaculture systems. However, its reliance on limited freshwater resources can lead to depletion, increased costs, and environmental stress, especially in arid regions. Efficient water management practices and the integration of alternative sources like greywater can optimize sustainability while maintaining productivity.
The Science Behind Greywater Recycling
Greywater recycling involves capturing and treating lightly used water from household activities such as bathing, laundry, and dishwashing to reduce freshwater demand in permaculture systems. Scientific research highlights that properly treated greywater can safely irrigate non-edible plants by removing pathogens and contaminants through filtration, biological treatment, and natural soil absorption processes. This sustainable water management practice enhances soil moisture retention and nutrient cycling while conserving freshwater resources critical for resilient agricultural ecosystems.
Comparative Water Efficiency: Greywater vs Freshwater
Greywater recycling significantly enhances water efficiency by reusing household wastewater for irrigation, reducing the demand for freshwater by up to 50%. Freshwater irrigation, while essential, consumes higher volumes and can strain local water resources, particularly in arid regions. Integrating greywater systems in permaculture design optimizes water usage, supports sustainable plant growth, and minimizes environmental impact.
Nutrient Content and Soil Health Impacts
Greywater recycling provides a sustainable source of water enriched with nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus that enhance soil fertility and promote microbial activity, improving overall soil health. Freshwater irrigation lacks these nutrients, often requiring additional fertilization to sustain plant growth and maintain soil structure. Utilizing greywater reduces freshwater demand while supporting nutrient cycling and soil organic matter accumulation in permaculture systems.
Safety Considerations and Best Practices
Greywater recycling in permaculture systems requires careful treatment to prevent pathogen exposure and nutrient imbalances, with best practices including the use of natural filtration methods such as constructed wetlands or sand filters. Freshwater irrigation offers lower health risks but demands sustainable sourcing and efficient use to conserve resources and avoid soil salinization. Integrating greywater reuse with appropriate crop selection and regular monitoring ensures safety while enhancing water conservation in permaculture designs.
System Installation and Maintenance Insights
Greywater recycling systems in permaculture require careful installation to ensure proper filtration and separation from blackwater, optimizing irrigation efficiency while reducing freshwater usage. Maintenance involves regular monitoring of filter media, pipes, and plant health to prevent clogging and contamination, which sustains system longevity and soil fertility. In contrast, freshwater irrigation systems have simpler installation but demand higher water resources and consistent management to avoid overwatering and soil degradation.
Environmental Impacts and Resource Conservation
Greywater recycling significantly reduces freshwater demand by reusing household wastewater for irrigation, decreasing stress on local water sources and minimizing nutrient runoff. Freshwater irrigation, while straightforward, often leads to over-extraction of aquifers and increased environmental degradation due to chemical fertilizers and pesticides entering ecosystems. Emphasizing greywater systems within permaculture helps conserve vital resources and promotes sustainable, low-impact gardening practices.
Choosing the Right Irrigation Method for Your Permaculture Garden
Greywater recycling maximizes resource efficiency by reusing household wastewater for irrigation, reducing freshwater consumption and supporting sustainable water management in permaculture gardens. Freshwater irrigation remains essential for sensitive plants requiring uncontaminated water, ensuring optimal growth and health in diverse ecosystems. Selecting the right irrigation method depends on plant tolerance, water availability, and regional regulations to maintain soil health and ecosystem balance effectively.
Greywater Recycling vs Freshwater Irrigation Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com