
Symmetrical Design vs Asymmetrical Design Illustration
Symmetrical design creates a balanced and harmonious appearance by mirroring elements on either side, often evoking a sense of order and stability in ornamental patterns. Asymmetrical design, on the other hand, offers a dynamic and visually intriguing composition, utilizing uneven distribution of elements to capture attention and convey movement. Both styles enhance ornamental aesthetics by catering to different emotional responses and spatial needs.
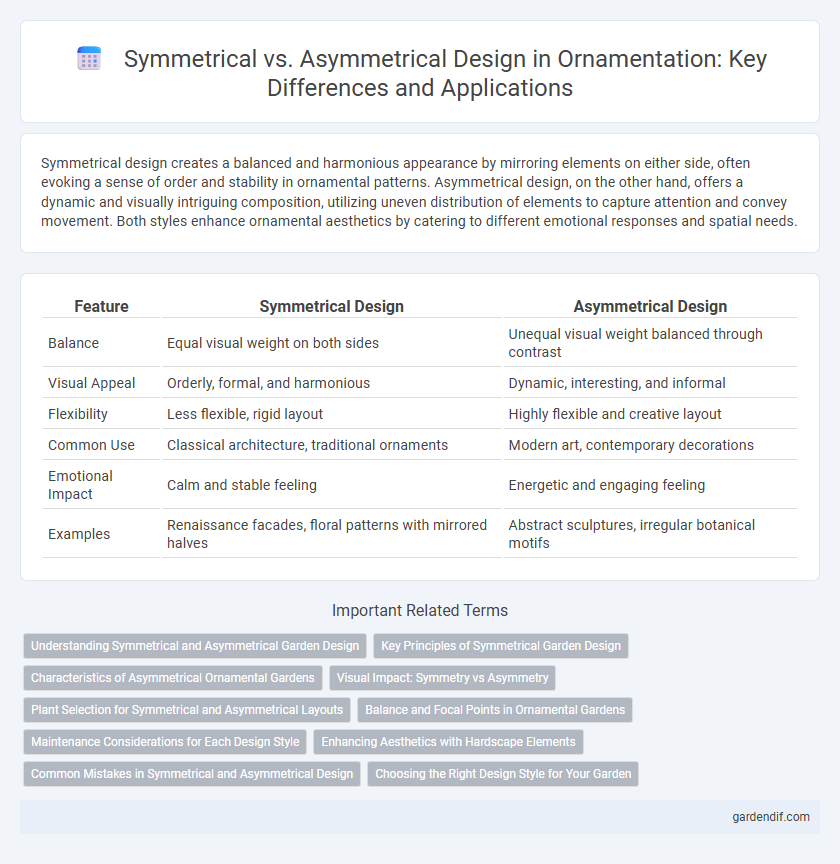
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Symmetrical Design | Asymmetrical Design |
|---|---|---|
| Balance | Equal visual weight on both sides | Unequal visual weight balanced through contrast |
| Visual Appeal | Orderly, formal, and harmonious | Dynamic, interesting, and informal |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, rigid layout | Highly flexible and creative layout |
| Common Use | Classical architecture, traditional ornaments | Modern art, contemporary decorations |
| Emotional Impact | Calm and stable feeling | Energetic and engaging feeling |
| Examples | Renaissance facades, floral patterns with mirrored halves | Abstract sculptures, irregular botanical motifs |
Understanding Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Garden Design
Symmetrical garden design emphasizes balance by mirroring elements on either side of a central axis, creating a formal and orderly appearance ideal for classical and traditional landscapes. Asymmetrical garden design relies on the strategic placement of different-sized elements to achieve visual harmony without exact duplication, offering a more natural and dynamic feel suited for contemporary and informal garden styles. Understanding these principles helps gardeners create spaces that evoke desired moods and enhance spatial perception through deliberate structuring of plants, pathways, and decorative features.
Key Principles of Symmetrical Garden Design
Symmetrical garden design emphasizes balance and harmony through mirrored elements on either side of a central axis, creating a formal and structured aesthetic. Key principles include uniform plant placement, identical shapes, and equal spacing to establish visual stability and order. This approach often incorporates geometric shapes, pathways, and focal points to reinforce the sense of symmetry and elegance.
Characteristics of Asymmetrical Ornamental Gardens
Asymmetrical ornamental gardens display a dynamic balance by arranging plants and features of varying sizes and shapes unevenly, creating a natural, informal aesthetic. These gardens often emphasize diversity in textures, colors, and heights, promoting visual interest without strict uniformity or repetition. The design encourages exploration and spontaneity, enhancing the garden's organic and artistic appeal.
Visual Impact: Symmetry vs Asymmetry
Symmetrical design creates visual harmony and balance by evenly distributing elements, which evokes a sense of order and stability in ornamental patterns. Asymmetrical design generates dynamic visual interest through deliberate imbalance, drawing attention and creating a more engaging and complex aesthetic experience. Both approaches influence emotional response and perception, where symmetry often conveys calmness and formality, while asymmetry introduces movement and spontaneity.
Plant Selection for Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Layouts
Symmetrical design in ornamental landscaping emphasizes balanced plant selection, favoring identical species or varieties placed opposite each other to create harmony and formal structure. Asymmetrical design incorporates diverse plant species with varying shapes, sizes, and textures, promoting visual interest and a natural, dynamic flow. Choosing plants with contrasting foliage and forms enhances the appeal of asymmetrical layouts, while uniform species reinforce the cohesive look of symmetrical designs.
Balance and Focal Points in Ornamental Gardens
Symmetrical design in ornamental gardens emphasizes balance by mirroring elements on either side of a central axis, creating a harmonious and formal aesthetic that naturally guides the eye to a strong central focal point such as a statue or fountain. Asymmetrical design achieves balance through varied visual weights, using diverse plant groupings, textures, and colors to create dynamic focal points that stimulate interest and movement without uniformity. Both approaches strategically manipulate spatial arrangement and visual emphasis to enhance the garden's overall composition and experiential flow.
Maintenance Considerations for Each Design Style
Symmetrical design in ornamental features offers easier maintenance due to its balanced and predictable layout, allowing for uniform pruning, cleaning, and repairs. Asymmetrical design often requires more detailed attention and customized care since the irregular shapes and varied elements can make upkeep more complex and time-consuming. Choosing symmetrical designs can reduce long-term maintenance efforts, while asymmetrical designs demand a more hands-on approach to preserve their intended aesthetic.
Enhancing Aesthetics with Hardscape Elements
Symmetrical design in hardscape elements creates balanced and harmonious outdoor spaces, emphasizing order and formality with evenly spaced features such as pathways, planters, and lighting. Asymmetrical design, on the other hand, introduces dynamic visual interest and natural flow by using irregular shapes and varied spatial arrangements, enhancing the organic feel of gardens and patios. Both approaches enhance aesthetics by strategically combining materials like stone, wood, and metal to complement the overall landscape architecture.
Common Mistakes in Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Design
Common mistakes in symmetrical design include overemphasis on uniformity, leading to monotonous or predictable layouts that lack visual interest. In asymmetrical design, errors often arise from poor balance, where elements feel disjointed or chaotic due to improper distribution of visual weight. Both designs require careful attention to harmony and proportion to avoid creating spaces that feel either too rigid or overly unstructured.
Choosing the Right Design Style for Your Garden
Symmetrical design in gardens emphasizes balance and order, featuring evenly spaced plants and mirrored elements that create a formal, structured look ideal for traditional settings. Asymmetrical design offers a more dynamic, natural feel by arranging plants and features unevenly while maintaining visual harmony, perfect for informal or modern garden styles. Choosing the right design style depends on the desired ambiance, space constraints, and personal preference, with symmetrical designs enhancing elegance and asymmetrical layouts fostering a relaxed, organic atmosphere.
Symmetrical Design vs Asymmetrical Design Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com