
Leaf mold vs peat moss Illustration
Leaf mold enriches soil by improving its structure and water retention through decomposed leaves, making it an excellent organic amendment for garden beds. Peat moss, derived from partially decayed sphagnum moss, also enhances moisture retention but has a lower nutrient content and raises soil acidity. Choosing between leaf mold and peat moss depends on the desired soil texture, pH preference, and sustainability considerations, with leaf mold being a more eco-friendly option.
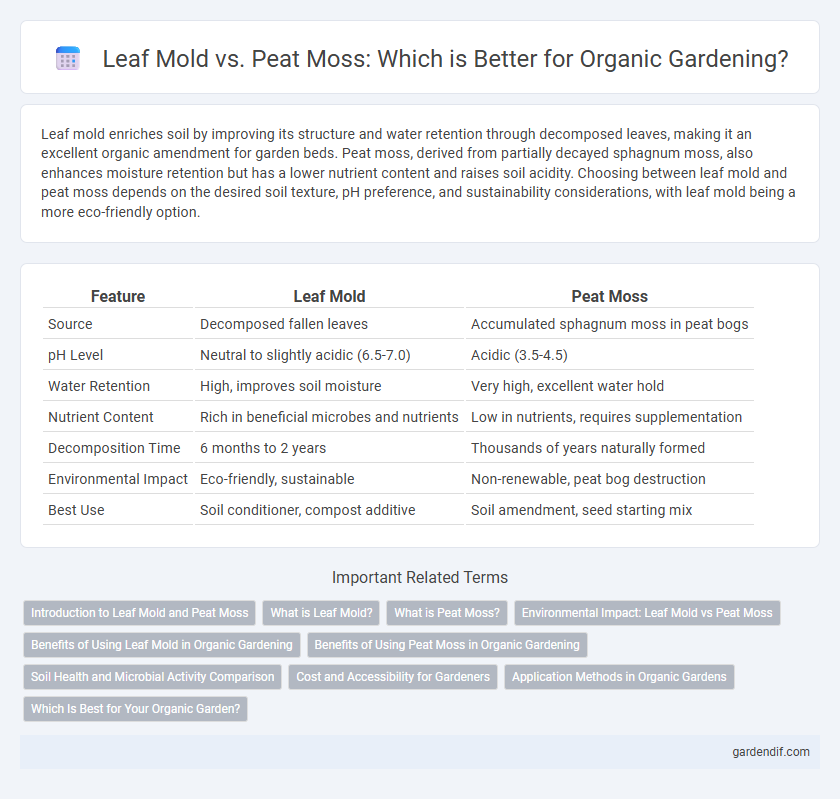
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Leaf Mold | Peat Moss |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Decomposed fallen leaves | Accumulated sphagnum moss in peat bogs |
| pH Level | Neutral to slightly acidic (6.5-7.0) | Acidic (3.5-4.5) |
| Water Retention | High, improves soil moisture | Very high, excellent water hold |
| Nutrient Content | Rich in beneficial microbes and nutrients | Low in nutrients, requires supplementation |
| Decomposition Time | 6 months to 2 years | Thousands of years naturally formed |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, sustainable | Non-renewable, peat bog destruction |
| Best Use | Soil conditioner, compost additive | Soil amendment, seed starting mix |
Introduction to Leaf Mold and Peat Moss
Leaf mold consists of decomposed leaves rich in beneficial fungi and organic matter that improves soil structure and moisture retention. Peat moss, derived from partially decomposed sphagnum moss in peat bogs, is valued for its high water-holding capacity and acidity regulation in soil. Both materials enhance soil fertility but differ significantly in origin, decomposition processes, and environmental impact.
What is Leaf Mold?
Leaf mold is a natural composting product created from decomposed fallen leaves, rich in beneficial fungi and organic matter that improves soil structure and moisture retention. Unlike peat moss, which is harvested from bogs and can contribute to habitat destruction, leaf mold is a sustainable resource that enhances soil fertility without disrupting ecosystems. Its slow decomposition process produces a nutrient-dense humus ideal for enriching garden beds and supporting healthy plant growth.
What is Peat Moss?
Peat moss is a type of partially decomposed sphagnum moss harvested from peat bogs, known for its excellent water retention and aeration properties. It is widely used in organic gardening to improve soil structure, increase moisture retention, and provide a lightweight growing medium for seedlings. Unlike leaf mold, peat moss is acidic with a low nutrient content, making it ideal for acid-loving plants such as blueberries and azaleas.
Environmental Impact: Leaf Mold vs Peat Moss
Leaf mold significantly reduces environmental impact by recycling fallen leaves into rich, natural compost, enhancing soil structure without depleting non-renewable resources. Peat moss harvesting contributes to carbon emissions and habitat destruction due to the slow regeneration rate of peat bogs, leading to long-term ecological damage. Choosing leaf mold supports sustainable gardening practices by preserving biodiversity and reducing carbon footprint compared to peat moss.
Benefits of Using Leaf Mold in Organic Gardening
Leaf mold improves soil structure by increasing moisture retention and promoting beneficial microbial activity, enhancing plant health naturally. It serves as an eco-friendly alternative to peat moss, reducing the environmental impact associated with peat extraction. Rich in decomposed organic matter, leaf mold supplies essential nutrients that support sustainable organic gardening practices.
Benefits of Using Peat Moss in Organic Gardening
Peat moss improves soil aeration and moisture retention, making it ideal for organic gardening by enhancing root development and water efficiency. Its acidic nature helps balance soil pH for acid-loving plants such as blueberries and azaleas. Peat moss also slowly decomposes, enriching the soil with organic matter and supporting beneficial microbial activity.
Soil Health and Microbial Activity Comparison
Leaf mold enhances soil health by improving moisture retention and promoting a diverse microbial ecosystem, which supports nutrient cycling and root development. Peat moss, while effective in water retention and soil aeration, tends to be more acidic and less nutrient-rich, potentially limiting microbial diversity and activity. The rich microbial presence in leaf mold accelerates organic matter decomposition, making it a superior choice for boosting soil vitality and fostering sustainable plant growth.
Cost and Accessibility for Gardeners
Leaf mold offers a cost-effective alternative to peat moss, as it can be collected from fallen leaves at little to no expense, making it highly accessible for gardeners. Peat moss, while widely available in garden centers, often comes at a higher price due to harvesting and processing costs, and its extraction raises environmental concerns. Gardeners seeking sustainable and affordable soil amendments increasingly prefer leaf mold for its abundance and minimal cost.
Application Methods in Organic Gardens
Leaf mold improves soil structure and moisture retention when incorporated as a top dressing or mixed into planting beds, enhancing microbial activity essential for organic gardens. Peat moss, commonly used to increase soil acidity and aeration, is best applied by blending it thoroughly with garden soil to avoid compaction and ensure root health. Both amendments support sustainable practices by enriching soil organic matter, but leaf mold provides a more environmentally friendly alternative due to its renewable nature.
Which Is Best for Your Organic Garden?
Leaf mold enhances soil structure and moisture retention through decomposed leaves, providing a nutrient-rich, slow-release organic matter ideal for sustainable gardening. Peat moss is valued for its acidity and water-holding capacity but poses environmental concerns due to its non-renewable extraction process. For an organic garden prioritizing eco-friendly practices and soil health, leaf mold is often the superior choice compared to peat moss.
Leaf mold vs peat moss Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com