
Pine Needles vs Leaf Litter Illustration
Pine needles create a lightweight, acidic mulch that improves soil drainage and prevents weed growth, making them ideal for acid-loving plants. Leaf litter, on the other hand, breaks down more quickly, enriching the soil with nutrients and supporting beneficial microorganisms. Choosing between pine needles and leaf litter depends on the specific needs of your garden's soil chemistry and desired nutrient cycling.
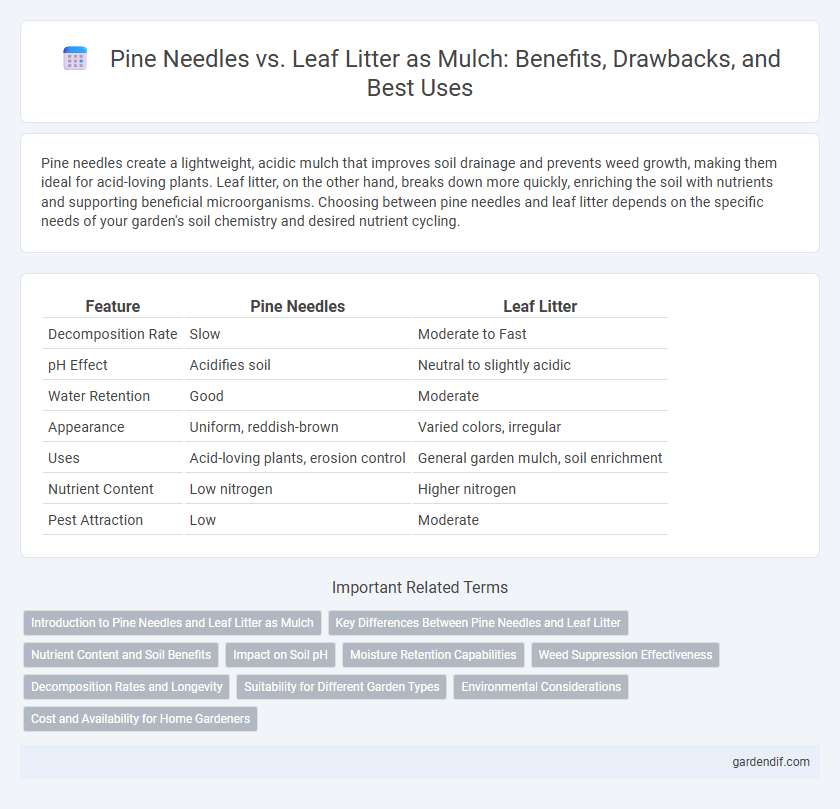
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pine Needles | Leaf Litter |
|---|---|---|
| Decomposition Rate | Slow | Moderate to Fast |
| pH Effect | Acidifies soil | Neutral to slightly acidic |
| Water Retention | Good | Moderate |
| Appearance | Uniform, reddish-brown | Varied colors, irregular |
| Uses | Acid-loving plants, erosion control | General garden mulch, soil enrichment |
| Nutrient Content | Low nitrogen | Higher nitrogen |
| Pest Attraction | Low | Moderate |
Introduction to Pine Needles and Leaf Litter as Mulch
Pine needles and leaf litter are natural mulch options that improve soil health and moisture retention in gardens. Pine needles, also known as pine straw, create a lightweight, acidic mulch ideal for acid-loving plants, while leaf litter decomposes quickly, enriching soil with organic matter and nutrients. Both mulches suppress weeds and regulate soil temperature, but their distinct decomposition rates and pH effects influence plant growth differently.
Key Differences Between Pine Needles and Leaf Litter
Pine needles create a lightweight, acidic mulch that decomposes slowly and helps improve soil acidity, ideal for acid-loving plants like azaleas and blueberries. Leaf litter, consisting of a diverse mix of broad leaves, breaks down faster, enriching soil with a wide range of nutrients and organic matter that benefits general garden plants. The key difference lies in decomposition rate and acidity impact, with pine needles providing long-lasting mulch and leaf litter offering faster nutrient cycling.
Nutrient Content and Soil Benefits
Pine needles provide acidic organic matter that gradually decomposes, improving soil structure and nutrient retention, particularly benefiting acid-loving plants like blueberries and azaleas. Leaf litter offers a higher nutrient content, including essential nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which enriches the soil more rapidly and supports diverse plant growth. Both mulches enhance moisture retention and microbial activity, but leaf litter's faster decomposition delivers quicker nutrient cycling compared to the slower, long-term benefits of pine needles.
Impact on Soil pH
Pine needles tend to acidify soil by releasing organic acids as they decompose, lowering soil pH and favoring acid-loving plants. In contrast, leaf litter generally has a neutral to slightly alkaline effect, maintaining or raising soil pH levels over time. Gardeners seeking to modify soil acidity can strategically choose pine needle mulch for acidification or leaf litter for balanced pH management.
Moisture Retention Capabilities
Pine needles provide excellent moisture retention by creating a loosely packed mulch layer that allows water to penetrate while reducing evaporation. In comparison, leaf litter forms a denser mat that can sometimes repel water, limiting deep soil moisture absorption. Both materials enhance soil moisture retention but pine needles typically offer better aeration alongside moisture conservation.
Weed Suppression Effectiveness
Pine needles provide superior weed suppression due to their acidic nature and dense mat formation, which inhibits weed seed germination more effectively than leaf litter. Leaf litter, while offering organic matter and nutrients, tends to break down quicker, allowing more light to reach the soil and consequently supporting weed growth. The slower decomposition rate and compact structure of pine needle mulch create a longer-lasting barrier against invasive plants.
Decomposition Rates and Longevity
Pine needles decompose more slowly than leaf litter due to their high lignin content and waxy coating, resulting in a longer-lasting mulch layer that retains soil moisture and suppresses weeds effectively. Leaf litter breaks down rapidly because of its softer texture and higher nitrogen content, enriching soil nutrients more quickly but requiring more frequent replacement. These contrasting decomposition rates make pine needles ideal for long-term soil protection, while leaf litter is better suited for fast nutrient cycling in garden beds.
Suitability for Different Garden Types
Pine needles provide excellent acidity and good drainage, making them ideal for acid-loving plants such as azaleas, blueberries, and rhododendrons in woodland or shade gardens. Leaf litter, rich in nutrients and organic matter, enhances soil fertility and moisture retention, suiting vegetable gardens, flower beds, and mixed perennial landscapes. Each mulch type supports specific garden ecosystems by promoting soil health and optimizing plant growth conditions.
Environmental Considerations
Pine needles decompose slowly, creating an acidic mulch that helps suppress weeds and conserve soil moisture, benefiting acid-loving plants while potentially altering soil pH and nutrient availability. Leaf litter breaks down faster, enriching soil with organic matter and nutrients, promoting biodiversity by supporting microorganisms and insects essential for healthy soil ecosystems. Choosing between pine needles and leaf litter depends on desired soil acidity, nutrient needs, and local ecosystem compatibility to maintain environmental sustainability.
Cost and Availability for Home Gardeners
Pine needles are generally more affordable and widely available in regions with coniferous trees, making them a cost-effective mulch option for home gardeners. Leaf litter, while often free and abundant in deciduous areas, may require more frequent replacement due to faster decomposition. Both mulches provide essential nutrients, but cost and consistent availability depend largely on local tree populations and seasonal leaf fall.
Pine Needles vs Leaf Litter Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com