
Succession planting vs single harvest Illustration
Succession planting maximizes harvest potential by allowing continuous crop production through staggered planting dates, ensuring fresh produce throughout the growing season. Single harvest methods concentrate planting and harvesting into one period, which can simplify management but may result in a limited supply window. Choosing succession planting enhances garden productivity and reduces downtime between crops compared to a single harvest approach.
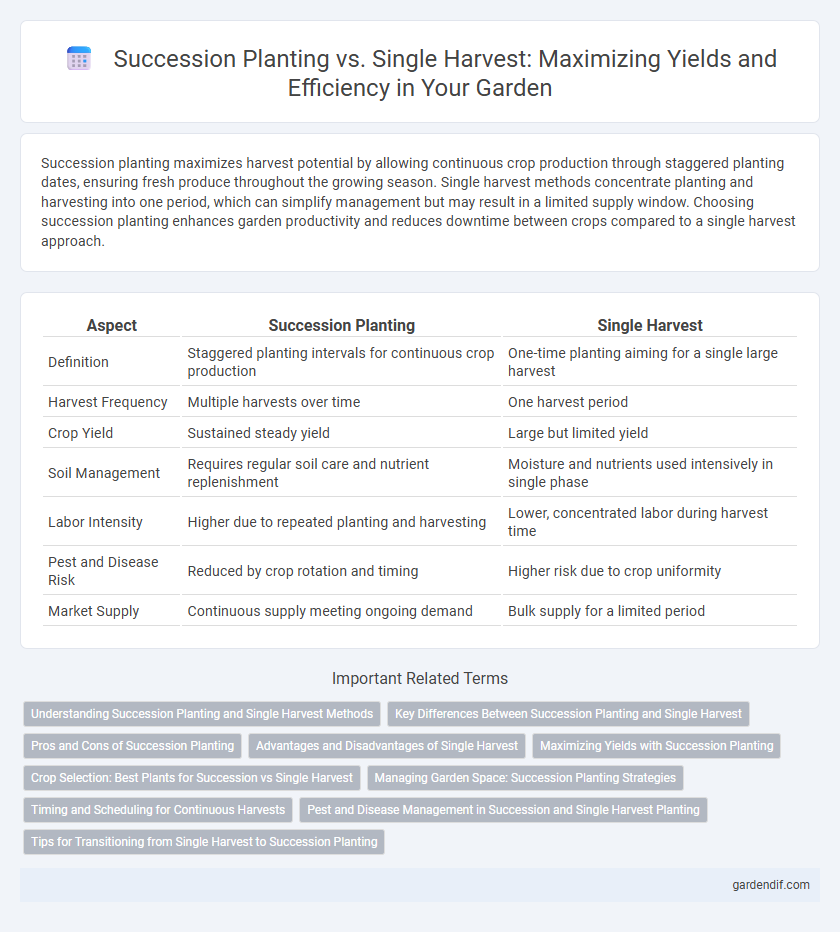
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Succession Planting | Single Harvest |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Staggered planting intervals for continuous crop production | One-time planting aiming for a single large harvest |
| Harvest Frequency | Multiple harvests over time | One harvest period |
| Crop Yield | Sustained steady yield | Large but limited yield |
| Soil Management | Requires regular soil care and nutrient replenishment | Moisture and nutrients used intensively in single phase |
| Labor Intensity | Higher due to repeated planting and harvesting | Lower, concentrated labor during harvest time |
| Pest and Disease Risk | Reduced by crop rotation and timing | Higher risk due to crop uniformity |
| Market Supply | Continuous supply meeting ongoing demand | Bulk supply for a limited period |
Understanding Succession Planting and Single Harvest Methods
Succession planting involves staggering crop plantings to ensure a continuous harvest throughout the growing season, maximizing garden productivity and reducing downtime. Single harvest methods focus on planting all seeds simultaneously, resulting in one large, concentrated yield that is easier to manage but less flexible. Understanding these methods allows gardeners to optimize space, labor, and harvest timing based on crop type and personal consumption needs.
Key Differences Between Succession Planting and Single Harvest
Succession planting involves sowing crops in intervals to ensure continuous harvests, while single harvest planting grows all crops simultaneously for one large yield. Key differences include timing efficiency, space utilization, and risk management; succession planting maximizes garden productivity by staggering growth, whereas single harvest simplifies planning but may lead to periods of inactivity. Selecting between methods depends on crop type, climate, and gardener goals for yield consistency and labor distribution.
Pros and Cons of Succession Planting
Succession planting offers the advantage of continuous crop production, maximizing garden yield by staggering planting times to ensure fresh harvests over an extended period. This method reduces the risk of total crop loss from pests or weather events by diversifying planting dates but requires more planning and maintenance compared to a single harvest approach. However, succession planting can demand more resources such as seeds, labor, and space, which may not be feasible for gardeners with limited time or area.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Single Harvest
Single harvest methods enable the growth of large, uniform crops that are harvested all at once, maximizing efficiency in planting and harvesting operations. However, this approach can lead to a glut of produce at harvest time, increasing storage requirements and the risk of spoilage if crops are not managed properly. Compared to succession planting, single harvest offers less flexibility in supply timing and may limit continuous fresh produce availability.
Maximizing Yields with Succession Planting
Succession planting increases overall crop yields by staggering planting times, enabling continuous harvests throughout the growing season rather than a single harvest peak. This method optimizes garden space utilization and reduces periods of soil exposure, improving soil health and nutrient cycling. By selecting fast-maturing varieties and carefully timing plantings, gardeners can sustain fresh produce availability and maximize productivity per square foot.
Crop Selection: Best Plants for Succession vs Single Harvest
Succession planting favors fast-maturing crops like lettuce, radishes, and spinach that can be harvested multiple times for a continuous yield. Single harvest crops such as pumpkins, corn, and winter squash require longer growing periods but produce one large, concentrated crop. Choosing crops with staggered maturity rates maximizes garden productivity and minimizes seasonal gaps in fresh produce availability.
Managing Garden Space: Succession Planting Strategies
Succession planting maximizes garden space by staggering crop sowing dates to ensure continuous harvests, reducing periods of soil idleness compared to single harvest methods. This strategy optimizes yield per square foot by overlapping growth cycles, which minimizes gaps and allows for efficient use of sunlight and nutrients. Implementing succession planting techniques enables gardeners to extend productive seasons and improve overall harvest frequency within limited spatial constraints.
Timing and Scheduling for Continuous Harvests
Succession planting involves staggered sowing of crops at regular intervals to ensure a continuous harvest, optimizing garden space and nutrient use over time. Single harvest planting, by contrast, grows crops all at once, resulting in a concentrated yield within a limited time frame. Precise timing and scheduling in succession planting maximize production by aligning crop maturity with demand and environmental conditions.
Pest and Disease Management in Succession and Single Harvest Planting
Succession planting reduces pest and disease buildup by interrupting pest life cycles and limiting host plant availability, lowering the risk of infestations compared to single harvest planting. Single harvest planting allows pests and diseases to accumulate on one crop batch, increasing vulnerability and potentially requiring more intensive pest management measures. Crop rotation and timely removal of infected plants are essential in both practices to enhance overall pest and disease control effectiveness.
Tips for Transitioning from Single Harvest to Succession Planting
Transitioning from single harvest to succession planting requires strategic planning to ensure continuous crop production and efficient space utilization. Begin by selecting fast-maturing varieties and staggering planting dates to maintain a steady yield throughout the growing season. Monitor soil health and nutrient levels closely to support successive crops and prevent depletion, enhancing overall garden productivity.
Succession planting vs single harvest Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com