
Succession Harvest vs Single Harvest Illustration
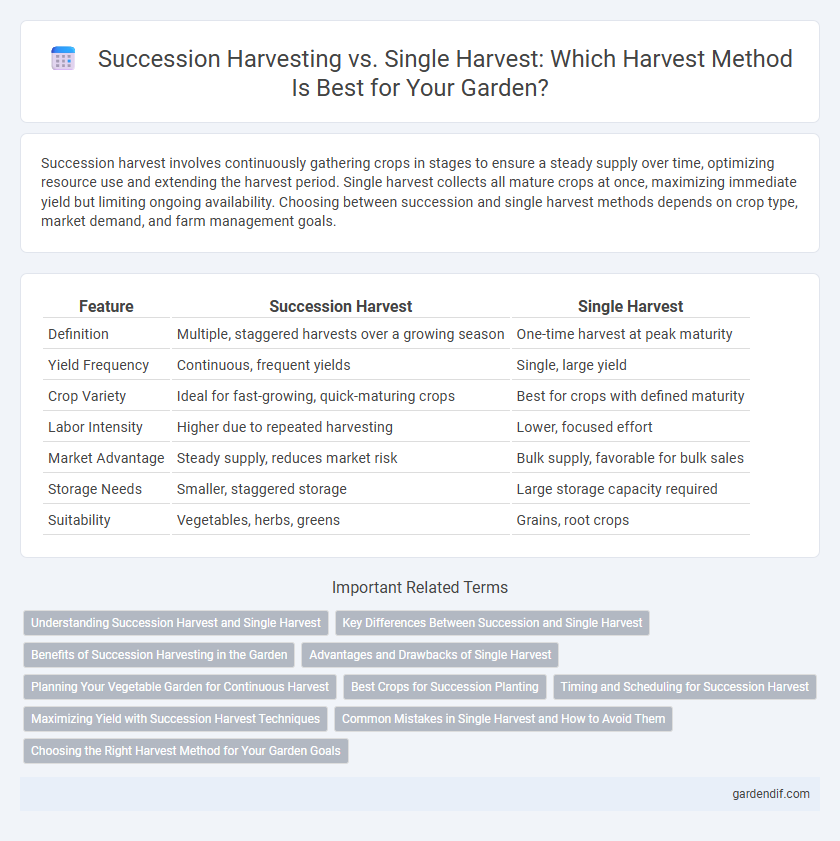
Succession harvest involves continuously gathering crops in stages to ensure a steady supply over time, optimizing resource use and extending the harvest period. Single harvest collects all mature crops at once, maximizing immediate yield but limiting ongoing availability. Choosing between succession and single harvest methods depends on crop type, market demand, and farm management goals.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Succession Harvest | Single Harvest |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multiple, staggered harvests over a growing season | One-time harvest at peak maturity |
| Yield Frequency | Continuous, frequent yields | Single, large yield |
| Crop Variety | Ideal for fast-growing, quick-maturing crops | Best for crops with defined maturity |
| Labor Intensity | Higher due to repeated harvesting | Lower, focused effort |
| Market Advantage | Steady supply, reduces market risk | Bulk supply, favorable for bulk sales |
| Storage Needs | Smaller, staggered storage | Large storage capacity required |
| Suitability | Vegetables, herbs, greens | Grains, root crops |
Understanding Succession Harvest and Single Harvest
Succession harvest involves cutting crops multiple times throughout the growing season to maximize yield and ensure continuous production, ideal for leafy greens and herbs. Single harvest refers to gathering the entire crop at once, commonly used for root vegetables and grains, optimizing labor and machinery efficiency. Understanding the differences helps farmers select the best method based on crop type, market demand, and resource availability.
Key Differences Between Succession and Single Harvest
Succession harvest involves multiple, staggered crops harvested over time, maximizing yield throughout the growing season and reducing risk of total crop failure. Single harvest is a one-time collection of mature crops, often resulting in a concentrated yield but requiring specific timing and labor effort. The key differences lie in harvest frequency, crop management, and resource allocation to optimize production and sustainability.
Benefits of Succession Harvesting in the Garden
Succession harvesting maximizes garden productivity by allowing continuous crop availability through staggered planting and picking schedules. This method reduces waste and ensures fresh produce over a longer period, improving nutrient intake and meal variety. Gardeners benefit from increased yields and efficient space usage compared to single harvests, which concentrate yields into one brief period.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Single Harvest
Single harvest farming allows for a concentrated, labor-efficient collection of crops at peak maturity, which can maximize immediate yield quality and reduce ongoing field maintenance costs. However, the drawback lies in its vulnerability to adverse weather or pest attacks during the brief harvest window, potentially resulting in total crop loss. This method also limits continuous income streams, as all produce is gathered once, unlike succession harvest systems which stagger planting and harvesting over time.
Planning Your Vegetable Garden for Continuous Harvest
Succession harvest involves planting vegetables at intervals to ensure a continuous supply of fresh produce throughout the growing season, maximizing garden productivity. Single harvest crops, on the other hand, mature all at once, requiring careful timing to avoid overripe or wasted vegetables. Efficient planning for succession planting, incorporating fast-maturing varieties and staggered sowing dates, optimizes yield and maintains a steady flow of vegetables for home gardeners.
Best Crops for Succession Planting
Succession harvest maximizes yields by planting best crops like leafy greens, radishes, and bush beans at intervals for continuous production, unlike single harvest crops such as corn or pumpkins that mature all at once. Fast-growing vegetables including lettuce, spinach, and carrots thrive in succession planting due to their short maturity cycles and reliable harvests. This method ensures a steady supply of fresh produce and helps optimize garden space throughout the growing season.
Timing and Scheduling for Succession Harvest
Succession harvest involves planting crops in intervals to ensure continuous yields over a longer season, optimizing timing and scheduling for steady production. This method requires careful planning to stagger planting dates, allowing crops to mature sequentially and providing a consistent supply. Unlike single harvest systems, succession harvest maximizes land use efficiency and reduces the risk of total crop failure by spreading out harvest times.
Maximizing Yield with Succession Harvest Techniques
Succession harvest techniques optimize crop yield by staggering planting and harvesting times, allowing continuous production throughout the growing season. Unlike single harvest methods that yield a single large crop, succession harvesting ensures steady market supply and reduces resource strain, maximizing land productivity. Implementing crop rotation and intercropping within succession harvesting further enhances soil health and yield efficiency.
Common Mistakes in Single Harvest and How to Avoid Them
Single harvest often suffers from common mistakes such as premature picking, which results in reduced yield and lower quality produce, and insufficient monitoring of crop maturity that can lead to uneven ripening. Avoiding these errors requires regular field inspections and precise timing based on crop-specific growth stages to ensure optimal flavor and nutritional content. Implementing a well-planned harvest schedule enhances efficiency, minimizes waste, and maximizes overall productivity compared to single harvest approaches.
Choosing the Right Harvest Method for Your Garden Goals
Succession harvest maximizes continuous crop yield by allowing multiple harvests over time, ensuring a steady supply of fresh produce tailored to ongoing garden needs. Single harvest focuses on gathering a full crop all at once, ideal for crops intended for preservation or large-scale immediate use. Selecting the right method depends on your garden goals, whether prioritizing consistent harvest intervals or bulk harvest efficiency.
Succession Harvest vs Single Harvest Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com