
Seed Maturity Harvest vs Immature Seed Harvest Illustration
Harvesting seeds at full maturity ensures maximum viability and optimal nutrient content, resulting in higher germination rates and better crop yields. In contrast, harvesting immature seeds often leads to lower seed quality, reduced storability, and diminished plant vigor. Proper timing during seed maturity is crucial for maintaining the genetic potential and overall success of future crops.
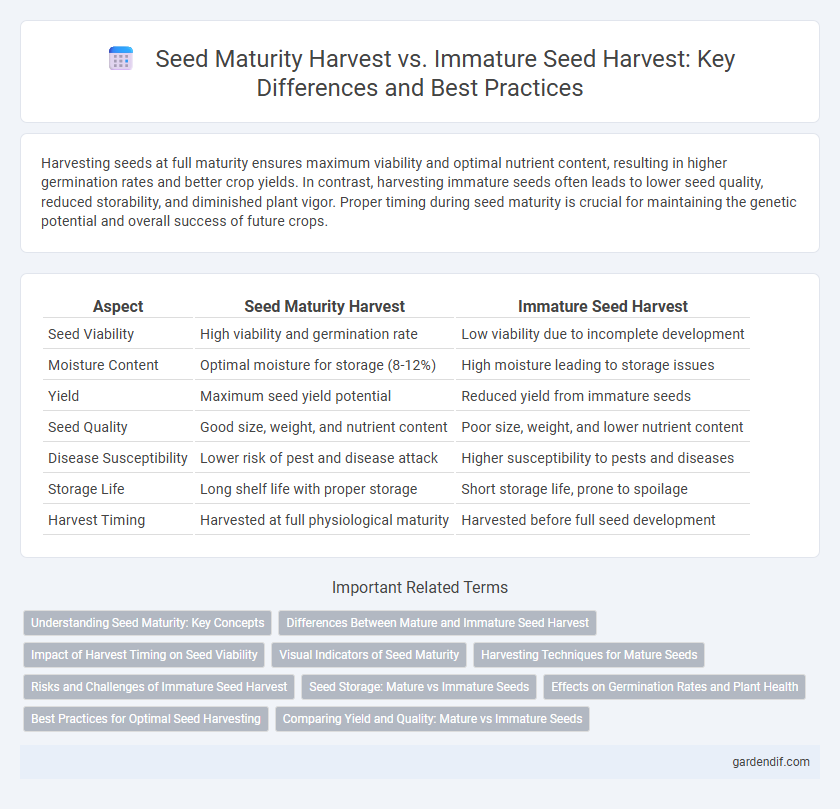
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Seed Maturity Harvest | Immature Seed Harvest |
|---|---|---|
| Seed Viability | High viability and germination rate | Low viability due to incomplete development |
| Moisture Content | Optimal moisture for storage (8-12%) | High moisture leading to storage issues |
| Yield | Maximum seed yield potential | Reduced yield from immature seeds |
| Seed Quality | Good size, weight, and nutrient content | Poor size, weight, and lower nutrient content |
| Disease Susceptibility | Lower risk of pest and disease attack | Higher susceptibility to pests and diseases |
| Storage Life | Long shelf life with proper storage | Short storage life, prone to spoilage |
| Harvest Timing | Harvested at full physiological maturity | Harvested before full seed development |
Understanding Seed Maturity: Key Concepts
Seed maturity is crucial for maximizing crop yield and quality, as mature seeds possess optimal nutrient content, viability, and germination potential. Harvesting immature seeds often results in lower germination rates, reduced vigor, and diminished storage life due to incomplete physiological development. Understanding seed maturity involves assessing moisture content, seed color, and hardness to determine the ideal harvest time for ensuring seed performance and successful propagation.
Differences Between Mature and Immature Seed Harvest
Harvesting mature seeds ensures higher germination rates and better seedling vigor compared to immature seed harvest, which often results in reduced viability and weaker plant development. Mature seeds have fully developed embryos and optimal nutrient reserves, critical for successful propagation and yield stability. Immature seeds contain higher moisture content and incomplete physiological growth, leading to increased susceptibility to diseases and poor storage longevity.
Impact of Harvest Timing on Seed Viability
Harvesting seeds at maturity ensures optimal seed viability, as fully developed seeds contain maximum nutrient reserves and genetic potential for germination. Immature seed harvest often results in reduced germination rates due to incomplete embryo development and lower moisture content, compromising seed vigor. Precise timing of harvest is critical to maintain seed quality, prevent dormancy issues, and maximize agricultural productivity.
Visual Indicators of Seed Maturity
Visual indicators of seed maturity include uniform seed color development, hardened seed coat, and reduced seed moisture content, which are critical for optimal harvest timing. Immature seeds typically display green coloration, soft coats, and higher moisture levels, leading to poor germination and lower yield quality. Observing pod and seed characteristics such as full size, a dulling pod surface, and seed firmness ensures selection of mature seeds for efficient harvesting.
Harvesting Techniques for Mature Seeds
Harvesting techniques for mature seeds prioritize precise timing to ensure optimal germination rates and seed viability. Mechanical harvesters calibrated for moisture content effectively reduce seed damage and increase collection efficiency. Optimal drying methods post-harvest preserve seed quality, preventing fungal growth and maintaining nutrient integrity.
Risks and Challenges of Immature Seed Harvest
Harvesting seeds before they reach full maturity poses significant risks including reduced germination rates, lower seed viability, and increased susceptibility to diseases and pests. Immature seed harvest can lead to poor crop establishment and diminished yield potential, impacting overall agricultural productivity. Managing moisture content and ensuring optimal harvest timing are critical challenges to prevent quality degradation in seeds collected prematurely.
Seed Storage: Mature vs Immature Seeds
Mature seeds exhibit enhanced storage longevity due to fully developed protective coatings and lower moisture content, which reduce the risk of fungal growth and deterioration. In contrast, immature seeds contain higher moisture and less stable cellular structures, leading to rapid quality loss and reduced viability during storage. Optimal seed storage practices prioritize harvesting at seed maturity to maximize germination rates and ensure seed vigor over extended periods.
Effects on Germination Rates and Plant Health
Harvesting seeds at full maturity significantly enhances germination rates by ensuring optimal nutrient reserves and embryo development, whereas immature seed harvest results in lower viability and reduced seedling vigor. Mature seeds exhibit stronger plant health due to better-established root systems and improved resistance to environmental stressors. Immature seeds often lead to weak seedlings prone to diseases and poor growth performance, negatively impacting crop yield and sustainability.
Best Practices for Optimal Seed Harvesting
Harvesting seeds at maturity ensures maximum viability, germination rates, and nutrient content, while immature seed harvest often results in lower quality and reduced storage potential. Best practices for optimal seed harvesting include monitoring seed moisture content, timing harvest to coincide with peak seed development, and employing gentle threshing techniques to minimize damage. Proper drying and storage environments further preserve seed longevity and performance, supporting successful future crop production.
Comparing Yield and Quality: Mature vs Immature Seeds
Harvesting mature seeds results in significantly higher yield and superior quality compared to immature seeds, as mature seeds contain fully developed nutrient reserves and optimal moisture content. Immature seed harvest typically leads to reduced germination rates and lower seed vigor, negatively impacting crop performance and long-term storage potential. Choosing the right harvest time based on seed maturity enhances overall agricultural productivity and market value.
Seed Maturity Harvest vs Immature Seed Harvest Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com