
Germination Rate vs Germination Speed Illustration
Germination rate refers to the percentage of seeds that successfully sprout within a given period, indicating overall seed viability. Germination speed measures the time it takes for seeds to begin sprouting, reflecting the rapidity of seed response under favorable conditions. Both factors are critical for evaluating seed performance and optimizing planting strategies.
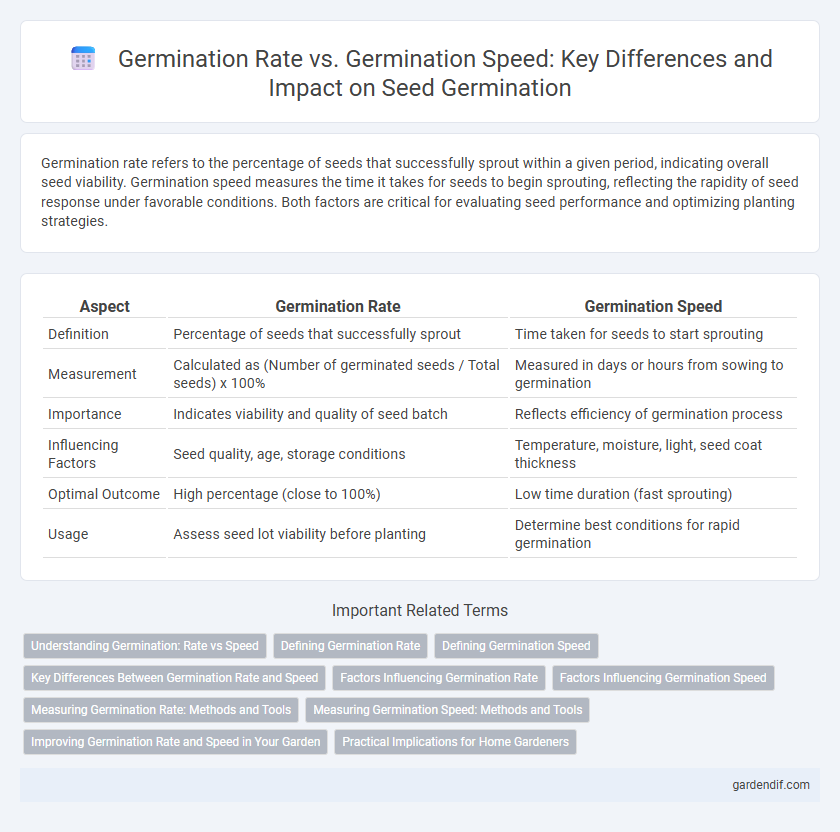
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Germination Rate | Germination Speed |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Percentage of seeds that successfully sprout | Time taken for seeds to start sprouting |
| Measurement | Calculated as (Number of germinated seeds / Total seeds) x 100% | Measured in days or hours from sowing to germination |
| Importance | Indicates viability and quality of seed batch | Reflects efficiency of germination process |
| Influencing Factors | Seed quality, age, storage conditions | Temperature, moisture, light, seed coat thickness |
| Optimal Outcome | High percentage (close to 100%) | Low time duration (fast sprouting) |
| Usage | Assess seed lot viability before planting | Determine best conditions for rapid germination |
Understanding Germination: Rate vs Speed
Germination rate measures the percentage of seeds that successfully sprout within a given period, indicating overall seed viability and health. Germination speed refers to how quickly seeds begin to sprout after planting, influencing crop timing and early growth stages. Understanding the distinction between germination rate and speed helps optimize planting strategies for improved crop yield and resource management.
Defining Germination Rate
Germination rate refers to the proportion of seeds that successfully sprout over a given period, providing a key metric for seed viability and crop yield predictions. It is often expressed as a percentage, calculated by dividing the number of germinated seeds by the total number of seeds tested. This rate differs from germination speed, which measures the time taken for seeds to begin sprouting after sowing.
Defining Germination Speed
Germination speed refers to the time it takes for seeds to begin sprouting after planting, often measured in days or hours to radicle emergence. Unlike germination rate, which quantifies the percentage of seeds that successfully germinate, germination speed emphasizes the rapidity and uniformity of seedling development. Faster germination speed indicates more vigorous seed vigor and can significantly impact overall crop establishment and productivity.
Key Differences Between Germination Rate and Speed
Germination rate measures the percentage of seeds that successfully sprout within a given timeframe, reflecting overall seed viability. Germination speed refers to the time taken for seeds to begin sprouting, indicating how quickly seeds initiate growth. Key differences include rate focusing on quantity of successful germinations, while speed emphasizes the rapidity of initial sprouting events.
Factors Influencing Germination Rate
Germination rate is influenced by factors such as seed quality, temperature, moisture levels, and oxygen availability, which collectively determine the percentage of seeds that successfully sprout over a given period. Optimal temperature ranges promote enzymatic activities essential for seed metabolism, while adequate moisture facilitates imbibition critical for cell expansion. Oxygen availability regulates respiration efficiency, directly impacting energy production necessary for germination speed and overall seedling vigor.
Factors Influencing Germination Speed
Germination speed is primarily influenced by factors such as seed moisture content, temperature, and oxygen availability, which directly affect enzymatic activity and metabolic rates essential for seed development. Soil quality, including pH and nutrient levels, also plays a crucial role in determining how quickly seeds break dormancy and begin growth. Understanding these variables helps optimize conditions for faster germination, enhancing crop uniformity and yield.
Measuring Germination Rate: Methods and Tools
Measuring germination rate involves calculating the percentage of seeds that successfully sprout within a specified period, providing insight into seed viability and quality. Methods for assessing germination rate include the standard germination test, tetrazolium test, and accelerated aging test, each utilizing controlled environmental conditions and precise time intervals. Tools such as germination chambers, paper towels or blotters, and imaging software assist in monitoring and recording germination progress to ensure accurate and reproducible results.
Measuring Germination Speed: Methods and Tools
Measuring germination speed involves recording the time required for seeds to sprout within a given sample using tools like germination trays and time-lapse imaging devices. Techniques such as the Mean Germination Time (MGT) and Germination Rate Index (GRI) calculate average days to germination and seedling emergence rates, providing quantitative data on seed performance. Advanced software applications facilitate precision in tracking germination events, enhancing the accuracy of speed assessments in agricultural research.
Improving Germination Rate and Speed in Your Garden
Improving germination rate and speed in your garden involves optimizing seed quality, soil temperature, moisture, and aeration. Using fresh, high-quality seeds and maintaining consistent warmth between 65-75degF accelerates seedling emergence while reducing the risk of fungal diseases. Proper watering techniques and well-drained soil ensure seeds receive adequate oxygen, promoting faster sprouting and higher overall germination success.
Practical Implications for Home Gardeners
A high germination rate ensures more seeds develop into healthy seedlings, maximizing crop yield in home gardens. Germination speed affects how quickly seedlings emerge, influencing planting schedules and resource allocation such as water and light. Home gardeners benefit from selecting seed varieties with both high germination rates and faster germination speeds to optimize growth cycles and harvest times.
Germination Rate vs Germination Speed Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com