
Mosaic virus vs Ring spot Illustration
Mosaic virus causes irregular, mottled patterns of light and dark green on leaves, leading to stunted growth and reduced crop yield. Ring spot typically presents as circular, necrotic lesions on leaves or fruits, which can severely damage plant tissues and affect overall plant health. Both diseases are viral and require specific management strategies to prevent widespread infection in agricultural settings.
Table of Comparison
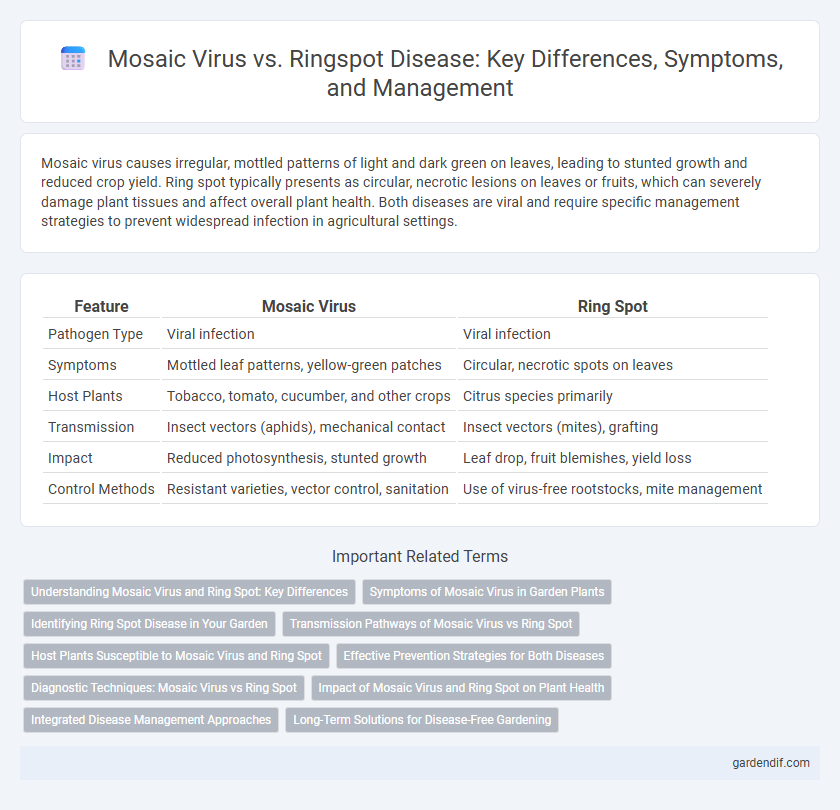
| Feature | Mosaic Virus | Ring Spot |
|---|---|---|
| Pathogen Type | Viral infection | Viral infection |
| Symptoms | Mottled leaf patterns, yellow-green patches | Circular, necrotic spots on leaves |
| Host Plants | Tobacco, tomato, cucumber, and other crops | Citrus species primarily |
| Transmission | Insect vectors (aphids), mechanical contact | Insect vectors (mites), grafting |
| Impact | Reduced photosynthesis, stunted growth | Leaf drop, fruit blemishes, yield loss |
| Control Methods | Resistant varieties, vector control, sanitation | Use of virus-free rootstocks, mite management |
Understanding Mosaic Virus and Ring Spot: Key Differences
Mosaic virus primarily affects plants by causing mottled patterns and discoloration on leaves, leading to reduced photosynthesis and stunted growth, with common hosts including cucumbers, tomatoes, and tobacco. Ring spot, caused by different viruses or fungi, manifests as circular lesions or spots on leaves and fruits, often resulting in tissue necrosis and diminished crop yield. Differentiating mosaic virus from ring spot involves examining symptom patterns, host specificity, and diagnostic tests such as ELISA or PCR for accurate disease management.
Symptoms of Mosaic Virus in Garden Plants
Mosaic virus in garden plants causes mottled or patchy discoloration on leaves, often featuring light and dark green areas that create a mosaic-like pattern. Infected plants may exhibit distorted leaf shape, curling, and stunted growth, severely affecting overall plant health and yield. These symptoms differentiate Mosaic virus from Ring spot, which typically presents as circular or oval lesions without the characteristic mosaic pattern.
Identifying Ring Spot Disease in Your Garden
Ring Spot Disease presents as circular, discolored lesions on leaves and fruits, often exhibiting a distinct target-like pattern, making it distinguishable from Mosaic virus which typically causes mottled, patchy discoloration. Gardeners can identify Ring Spot Disease by looking for brown or yellow rings that gradually enlarge and may coalesce, leading to leaf distortion and reduced fruit quality. Early detection involves closely examining symptomatic plants and consulting local extension services for accurate diagnosis and management options.
Transmission Pathways of Mosaic Virus vs Ring Spot
Mosaic virus primarily spreads through mechanical injury, contaminated tools, and insect vectors such as aphids, enabling rapid transmission between plants. Ring spot disease, often caused by fungal or viral agents, transmits mainly via infected plant debris, soil, and sometimes seed-borne pathways. Understanding these distinct transmission routes is critical for effective disease management and control strategies in agricultural settings.
Host Plants Susceptible to Mosaic Virus and Ring Spot
Mosaic virus primarily affects cucurbits such as cucumbers, melons, and squash, causing mottled leaf patterns and stunted growth. Ring spot commonly infects stone fruit trees including peaches, cherries, and plums, leading to circular lesions on leaves and fruit. Both viruses significantly reduce yield and quality in their respective susceptible host plants.
Effective Prevention Strategies for Both Diseases
Controlling Mosaic virus and Ring spot relies heavily on integrated pest management including the use of resistant crop varieties and rigorous crop rotation to reduce viral reservoirs. Implementing strict sanitation practices such as removing infected plants and disinfecting tools helps prevent virus spread in both cases. Vector control targeting aphids and beetles also plays a critical role in minimizing transmission of these plant viruses.
Diagnostic Techniques: Mosaic Virus vs Ring Spot
Diagnostic techniques for Mosaic virus primarily involve ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) and PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) to detect viral RNA with high specificity. Ring spot diagnosis often relies on symptom observation combined with molecular methods like RT-PCR to differentiate it from other viral infections. Advanced serological assays and nucleic acid hybridization enhance accuracy in distinguishing Mosaic virus from Ring spot disease in crops.
Impact of Mosaic Virus and Ring Spot on Plant Health
Mosaic virus causes mottled, discolored leaves that reduce photosynthesis efficiency, stunting plant growth and lowering crop yields significantly. Ring spot leads to circular spots and lesions on leaves and fruits, disrupting nutrient flow and increasing susceptibility to secondary infections. Both diseases severely compromise plant health, leading to weakened plants and reduced agricultural productivity.
Integrated Disease Management Approaches
Integrated Disease Management (IDM) for Mosaic virus and Ring spot involves combining cultural practices, resistant varieties, and targeted chemical treatments to reduce disease impact on crops. Crop rotation and removal of infected plant debris minimize viral reservoirs, while early detection through field scouting supports timely interventions. Use of certified virus-free seeds and vector control, such as managing aphid populations, further enhances disease suppression and crop health.
Long-Term Solutions for Disease-Free Gardening
Implementing crop rotation and planting resistant cultivars significantly reduces the incidence of Mosaic virus and Ring spot, promoting disease-free gardening over the long term. Utilizing certified virus-free seeds and removing infected plants promptly minimizes viral reservoirs and spread within the garden. Integrating effective vector control and maintaining proper sanitation practices further enhances sustainable management of these plant viruses.
Mosaic virus vs Ring spot Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com