
Leaf Spot vs Leaf Blotch Illustration
Leaf spot and leaf blotch are common fungal diseases affecting plants, with leaf spot characterized by small, distinct circular or irregular spots, often with a darker border. In contrast, leaf blotch presents larger, more diffuse lesions that may coalesce, causing extensive tissue damage and discoloration. Both conditions hinder photosynthesis and can lead to significant yield loss if not managed promptly.
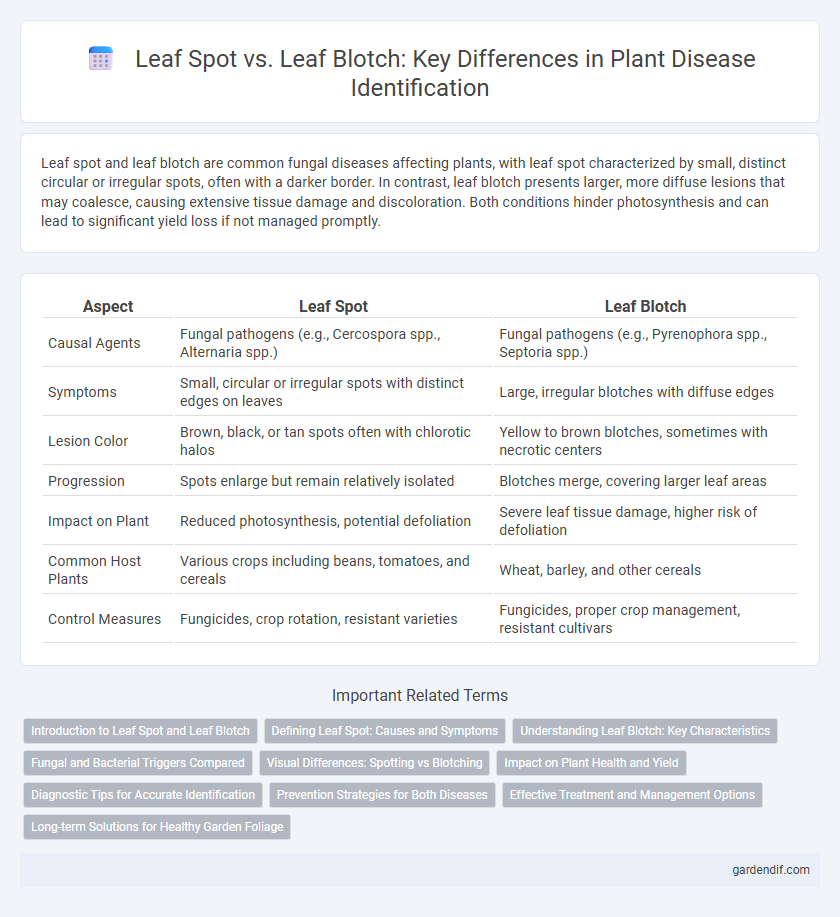
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Leaf Spot | Leaf Blotch |
|---|---|---|
| Causal Agents | Fungal pathogens (e.g., Cercospora spp., Alternaria spp.) | Fungal pathogens (e.g., Pyrenophora spp., Septoria spp.) |
| Symptoms | Small, circular or irregular spots with distinct edges on leaves | Large, irregular blotches with diffuse edges |
| Lesion Color | Brown, black, or tan spots often with chlorotic halos | Yellow to brown blotches, sometimes with necrotic centers |
| Progression | Spots enlarge but remain relatively isolated | Blotches merge, covering larger leaf areas |
| Impact on Plant | Reduced photosynthesis, potential defoliation | Severe leaf tissue damage, higher risk of defoliation |
| Common Host Plants | Various crops including beans, tomatoes, and cereals | Wheat, barley, and other cereals |
| Control Measures | Fungicides, crop rotation, resistant varieties | Fungicides, proper crop management, resistant cultivars |
Introduction to Leaf Spot and Leaf Blotch
Leaf Spot and Leaf Blotch are common fungal diseases affecting a variety of plants, characterized by distinct lesions on foliage. Leaf Spot manifests as small, circular to irregular spots, often with a defined border, primarily caused by pathogens like Cercospora and Alternaria species. Leaf Blotch appears as larger, elongated, or blotchy patches on leaves, typically resulting from fungi such as Septoria or Stagonospora, leading to significant defoliation and crop yield reduction.
Defining Leaf Spot: Causes and Symptoms
Leaf spot is a common plant disease characterized by small, discolored lesions on leaves caused primarily by fungal pathogens such as Cercospora and Bipolaris species. Symptoms include circular or irregularly shaped spots with defined margins, often brown, black, or tan, sometimes surrounded by yellow halos indicating tissue damage. Moist and warm environmental conditions favor the development and spread of leaf spot, leading to premature leaf drop and reduced photosynthetic capacity.
Understanding Leaf Blotch: Key Characteristics
Leaf blotch manifests as irregular, angular brown or tan lesions with distinct margins, contrasting the more rounded spots typical of leaf spot disease. It commonly affects cereal crops such as wheat and barley, causing premature leaf senescence and significant yield reduction. Understanding the pathogen Septoria tritici, which causes leaf blotch, enables targeted fungicide application and effective disease management strategies.
Fungal and Bacterial Triggers Compared
Leaf spot and leaf blotch diseases differ primarily in their fungal and bacterial triggers, with leaf spot often caused by fungal pathogens such as Cercospora, Septoria, and Alternaria species, while leaf blotch is frequently associated with fungal agents like Pyrenophora and bacterial pathogens including Xanthomonas spp. Both diseases manifest as lesions on foliage, but fungal leaf spots typically produce smaller, more defined circular spots compared to the larger, irregular blotches caused by mixed fungal and bacterial infections in leaf blotch. Effective management requires accurate pathogen identification to target specific agrochemicals and cultural practices tailored to fungal or bacterial etiology for each disease.
Visual Differences: Spotting vs Blotching
Leaf spot presents as small, round or irregularly shaped lesions with well-defined edges, often exhibiting a distinct border and varying colors such as brown, black, or yellow. Leaf blotch appears as larger, irregularly shaped patches that merge together, creating extensive areas of discoloration with less defined margins compared to spots. The visual distinction lies in the isolated, pinpointed damage of leaf spots versus the expansive, diffuse damage characteristic of leaf blotch.
Impact on Plant Health and Yield
Leaf spot disease causes small, circular lesions that impair photosynthesis by damaging leaf tissue, leading to reduced plant vigor and moderate yield loss. Leaf blotch results in larger, irregularly shaped necrotic areas that can coalesce, severely compromising leaf function and causing significant reductions in crop yield. Both diseases weaken plants but leaf blotch typically exerts a greater negative impact on overall plant health and productivity.
Diagnostic Tips for Accurate Identification
Leaf Spot presents as small, well-defined circular or irregular lesions with dark brown or black edges, often surrounded by yellow halos, while Leaf Blotch typically shows larger, irregularly shaped, water-soaked patches that may coalesce and lack distinct borders. Accurate identification requires close examination of lesion size, shape, margin clarity, and discoloration patterns on affected foliage. Microscopic analysis and pathogen-specific testing, such as fungal culture or PCR assays, further confirm diagnosis by identifying the causative organisms responsible for each disease.
Prevention Strategies for Both Diseases
Implementing crop rotation and maintaining proper plant spacing reduces leaf wetness, limiting conditions favorable for both leaf spot and leaf blotch infections. Applying fungicides with proven efficacy during early disease stages helps prevent pathogen establishment and spread. Regular removal of infected plant debris minimizes inoculum sources, enhancing overall disease management.
Effective Treatment and Management Options
Effective treatment of Leaf Spot involves fungicides containing chlorothalonil or copper-based compounds, combined with proper sanitation such as removing infected leaves to prevent spores from spreading. Leaf Blotch management focuses on cultural practices like improving air circulation and reducing leaf wetness, alongside the application of systemic fungicides like myclobutanil for sustained protection. Integrated disease management strategies that include crop rotation, resistant plant varieties, and timely fungicide applications enhance control efficacy for both diseases.
Long-term Solutions for Healthy Garden Foliage
Leaf spot and leaf blotch diseases require targeted long-term solutions to ensure healthy garden foliage by improving plant resistance through disease-resistant cultivars and implementing crop rotation practices. Regular pruning and maintaining optimal air circulation reduce humidity, limiting fungal growth and disease spread. Incorporating organic mulches and practicing proper sanitation eliminate infected debris, minimizing pathogen reservoirs for subsequent seasons.
Leaf Spot vs Leaf Blotch Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com