
Damping-Off vs Root Rot Illustration
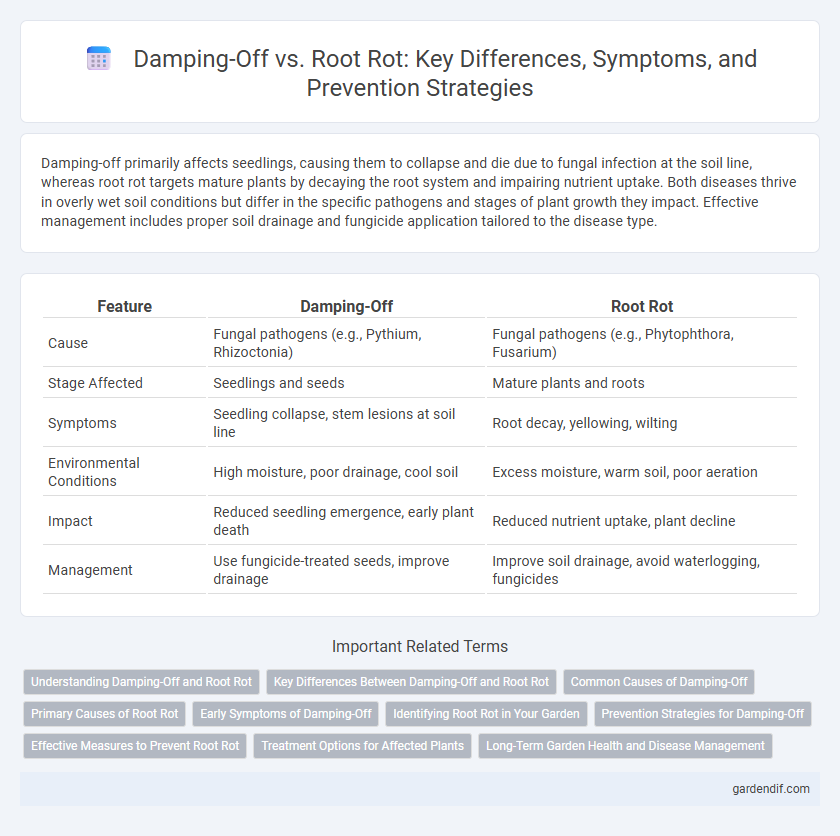
Damping-off primarily affects seedlings, causing them to collapse and die due to fungal infection at the soil line, whereas root rot targets mature plants by decaying the root system and impairing nutrient uptake. Both diseases thrive in overly wet soil conditions but differ in the specific pathogens and stages of plant growth they impact. Effective management includes proper soil drainage and fungicide application tailored to the disease type.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Damping-Off | Root Rot |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Fungal pathogens (e.g., Pythium, Rhizoctonia) | Fungal pathogens (e.g., Phytophthora, Fusarium) |
| Stage Affected | Seedlings and seeds | Mature plants and roots |
| Symptoms | Seedling collapse, stem lesions at soil line | Root decay, yellowing, wilting |
| Environmental Conditions | High moisture, poor drainage, cool soil | Excess moisture, warm soil, poor aeration |
| Impact | Reduced seedling emergence, early plant death | Reduced nutrient uptake, plant decline |
| Management | Use fungicide-treated seeds, improve drainage | Improve soil drainage, avoid waterlogging, fungicides |
Understanding Damping-Off and Root Rot
Damping-off primarily affects seedlings, causing them to collapse and die due to fungal pathogens like Pythium and Rhizoctonia attacking the stem base in overly moist soil conditions. Root rot, caused by various fungi such as Phytophthora and Fusarium, invades mature plant roots, leading to decay, impaired nutrient uptake, and overall plant decline. Differentiating symptoms include damping-off's sudden seedling failure versus root rot's gradual wilting and yellowing in established plants.
Key Differences Between Damping-Off and Root Rot
Damping-off primarily affects seedlings, causing stems to rot at soil level and leading to sudden plant collapse, whereas root rot targets mature plants, resulting in decayed roots and impaired nutrient uptake. The causative agents of damping-off are typically soilborne fungi like Pythium and Rhizoctonia, while root rot is often caused by pathogens such as Fusarium and Phytophthora species. Environmental conditions like excessive moisture and poor drainage exacerbate both diseases but manifest distinctly in plant symptoms and developmental stages.
Common Causes of Damping-Off
Damping-off is primarily caused by soil-borne pathogens such as Pythium, Rhizoctonia, and Fusarium species, which thrive in overly moist and poorly drained soil conditions. These pathogens attack seedlings at or just below the soil surface, leading to stem collapse and seedling death. In contrast, root rot often develops from prolonged pathogen activity in roots of mature plants, frequently linked to waterlogged soil and poor aeration.
Primary Causes of Root Rot
Root rot is primarily caused by soil-borne fungi such as Phytophthora, Pythium, and Rhizoctonia species, which thrive in overly wet, poorly drained soils that suffocate plant roots. These pathogens invade the root system, disrupting water and nutrient uptake, leading to impaired plant growth and eventual death. Unlike damping-off, which affects seedlings during germination, root rot impacts established plants by degrading root tissue and promoting secondary infections.
Early Symptoms of Damping-Off
Early symptoms of damping-off include seedling stem collapse near the soil line, water-soaked lesions, and poor germination. Unlike root rot, which typically causes discoloration and decay of mature root systems, damping-off affects young seedlings before or just after emergence. Identification of these initial signs is crucial for timely intervention and prevention of seedling loss.
Identifying Root Rot in Your Garden
Root rot in your garden can be identified by symptoms such as wilting, yellowing leaves, and a mushy, discolored root system. Unlike damping-off, which affects seedlings and causes sudden collapse, root rot typically develops more slowly and impacts mature plants. Inspect the roots for brown or black lesions and foul odor, which are key indicators of fungal infections like Phytophthora or Pythium species responsible for root rot.
Prevention Strategies for Damping-Off
Effective prevention strategies for damping-off include maintaining well-drained soil and avoiding overwatering to reduce excess moisture that promotes fungal growth. Sterilizing seeds and using fungicide-treated seeds can significantly decrease the incidence of soil-borne pathogens such as Pythium and Rhizoctonia. Crop rotation and proper spacing to improve air circulation further minimize the risk of damping-off in seedlings.
Effective Measures to Prevent Root Rot
Effective measures to prevent root rot include ensuring well-drained soil and avoiding overwatering to reduce excess moisture that fosters fungal growth. Using disease-resistant plant varieties and implementing crop rotation can minimize pathogen presence in the soil. Applying fungicides and maintaining proper sanitation by removing infected plant debris further helps in controlling root rot.
Treatment Options for Affected Plants
Treatment options for damping-off include removing infected seedlings, improving soil drainage, and applying fungicides like metalaxyl or thiophanate-methyl to prevent fungal spread. Root rot management involves enhancing soil aeration, avoiding overwatering, and using fungicides such as phosphorous acid or azoxystrobin to control pathogens like Phytophthora and Pythium. Both diseases benefit from sterilizing tools and practicing crop rotation to reduce soilborne inoculum levels.
Long-Term Garden Health and Disease Management
Damping-off primarily affects seedlings, causing rapid wilting and death, while root rot develops over time, leading to decayed roots and stunted growth in mature plants. Effective disease management combines well-drained soil, crop rotation, and fungicide treatments to prevent both conditions and promote long-term garden health. Maintaining balanced soil moisture and avoiding overwatering are critical strategies to reduce the risk of these fungal diseases and ensure sustained plant vitality.
Damping-Off vs Root Rot Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com