
Bacterial leaf spot vs Fungal leaf spot Illustration
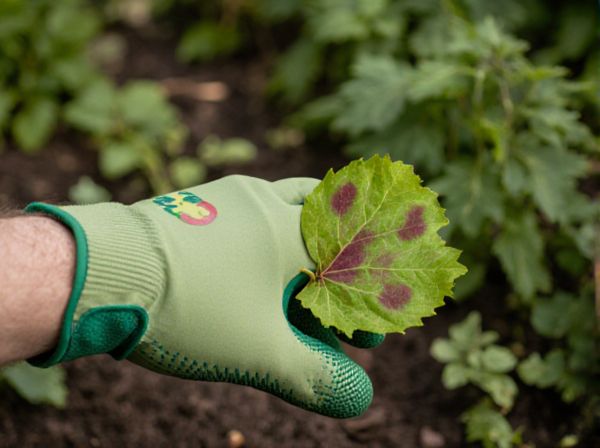
Bacterial leaf spot typically causes angular, water-soaked lesions that may ooze bacterial slime, whereas fungal leaf spot often appears as circular or irregularly shaped lesions with distinct dark borders. Bacterial infections spread rapidly in warm, wet conditions and produce a greasy appearance on affected leaves, while fungal leaf spots develop more slowly, often accompanied by fungal spores or fruiting bodies on the lesion surface. Effective management requires accurate diagnosis since bacterial leaf spot responds better to copper-based bactericides, while fungal leaf spot control relies on fungicides and cultural practices to reduce spore survival.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Bacterial Leaf Spot | Fungal Leaf Spot |
|---|---|---|
| Pathogen Type | Bacteria (e.g., Xanthomonas spp.) | Fungi (e.g., Cercospora spp., Alternaria spp.) |
| Symptoms | Water-soaked lesions, angular spots with yellow halos | Round to irregular spots with concentric rings or dark margins |
| Transmission | Water splashes, contaminated tools, infected seeds | Spores spread by wind, rain splash, plant debris |
| Environmental Conditions | Warm, wet conditions favor bacterial growth | Cool to warm, humid conditions with leaf wetness |
| Treatment | Use copper-based bactericides, crop rotation, sanitation | Apply fungicides, remove infected debris, improve air circulation |
| Host Range | Wide host range including vegetables and ornamental plants | Common in many crops, including fruits, vegetables, and ornamentals |
| Diagnosis | Microscopic examination, bacterial culture, PCR tests | Microscopic identification of fungal spores, culture, molecular tests |
Understanding Leaf Spot Diseases: Bacterial vs Fungal
Bacterial leaf spot diseases, caused by pathogens such as Xanthomonas or Pseudomonas species, typically produce water-soaked, angular lesions with a yellow halo, whereas fungal leaf spots, caused by fungi like Cercospora or Alternaria, often present as circular or irregularly shaped spots with concentric rings or a target-like appearance. Both bacterial and fungal leaf spots disrupt photosynthesis by damaging leaf tissue, leading to reduced plant vigor and yield loss in crops such as tomatoes, peppers, and beans. Effective disease management relies on accurate differentiation through symptom identification, pathogen testing, and implementing cultural practices such as crop rotation, resistant varieties, and appropriate use of bactericides or fungicides.
Key Symptoms: Identifying Bacterial and Fungal Leaf Spots
Bacterial leaf spot symptoms typically include water-soaked lesions that may appear greasy and often have irregular shapes with yellow halos, while fungal leaf spots usually present as dry, circular to irregular lesions with well-defined borders and concentric rings. Bacterial spots can cause leaf yellowing and premature leaf drop, whereas fungal spots often exhibit dark brown or black centers surrounded by a yellow or tan margin. Accurate identification relies on observing lesion texture, shape, and progression, which is critical for effective disease management in crops.
Causes and Transmission: Bacteria versus Fungi
Bacterial leaf spot is caused by pathogenic bacteria such as Xanthomonas spp., which enter plants primarily through natural openings or wounds, spreading via water splashes and contaminated tools. Fungal leaf spot results from various fungi like Cercospora and Alternaria species, transmitted through airborne spores, rain splash, and infected plant debris. Understanding these distinct pathogens and their transmission methods aids in developing targeted disease management strategies for effective control.
Plant Hosts Susceptible to Leaf Spot Diseases
Bacterial leaf spot primarily affects crops such as peppers, tomatoes, and beans, while fungal leaf spot commonly targets a broader range of plants including cucumbers, lettuce, and various ornamental species. Plant hosts susceptible to bacterial leaf spot often exhibit water-soaked lesions with angular shapes, whereas fungal leaf spot presents as circular spots with distinct concentric rings or a powdery growth. Understanding specific host-pathogen interactions is essential for developing effective disease management strategies in agricultural and horticultural systems.
How Bacterial Leaf Spot Develops and Spreads
Bacterial leaf spot develops when pathogenic bacteria infiltrate leaf tissue through natural openings, wounds, or insect damage, thriving in warm, wet conditions that promote rapid multiplication. The spread occurs primarily via water splashes, rain, irrigation, and contaminated tools or hands, enabling bacteria to infect nearby plants. High humidity and poor air circulation create optimal environments for outbreaks, intensifying the impact on crop health and yield.
How Fungal Leaf Spot Develops and Spreads
Fungal leaf spot develops through the germination of fungal spores on leaf surfaces, facilitated by moisture and favorable temperatures typically between 20-30degC. The fungi penetrate leaf tissues using specialized structures called appressoria, leading to characteristic necrotic lesions as the infection progresses. Spores produced in these lesions are dispersed by wind, rain splash, or contaminated tools, enabling rapid spread across plants and fields.
Diagnosis: Distinguishing Bacterial from Fungal Leaf Spots
Bacterial leaf spot typically presents with water-soaked lesions that often have a yellow halo, while fungal leaf spot features dry, brown or black lesions with well-defined edges. Microscopic examination reveals bacterial spots contain slimy bacterial ooze, whereas fungal spots show distinct fungal spores or mycelia. Laboratory tests such as PCR or culturing can further confirm the presence of bacterial pathogens like Xanthomonas or fungal pathogens like Cercospora, aiding precise diagnosis.
Effective Control and Management Strategies
Effective control of bacterial leaf spot primarily involves the use of copper-based bactericides and maintaining proper plant spacing to reduce leaf wetness, while fungal leaf spot is best managed through fungicides containing chlorothalonil or mancozeb combined with crop rotation and removal of infected debris. Implementing resistant plant varieties and practicing strict sanitation are critical in minimizing disease spread for both bacterial and fungal leaf spots. Consistent monitoring and early intervention enhance the effectiveness of these integrated pest management strategies.
Prevention Tips for Leaf Spot Diseases
Effective prevention of bacterial and fungal leaf spot diseases involves regular monitoring of plants for early symptoms such as water-soaked lesions in bacterial infections and powdery or necrotic spots in fungal cases. Implementing proper sanitation practices by removing infected leaves and avoiding overhead irrigation reduces moisture that promotes pathogen growth. Using disease-resistant plant varieties and applying appropriate fungicides or bactericides according to agricultural guidelines further minimizes the risk of severe outbreaks.
Integrated Disease Management for Healthy Gardens
Integrated Disease Management for bacterial and fungal leaf spot involves a combination of cultural, biological, and chemical strategies to maintain healthy gardens. Crop rotation, resistant plant varieties, proper irrigation techniques, and removal of infected leaves reduce the spread of Xanthomonas bacteria and fungal pathogens like Cercospora species. Applying targeted bactericides and fungicides, along with promoting beneficial microorganisms, enhances disease control and supports sustainable garden health.
Bacterial leaf spot vs Fungal leaf spot Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com