
Shallow pots vs deep pots Illustration
Shallow pots provide excellent drainage and are ideal for plants with shallow root systems, promoting healthier growth and reducing the risk of root rot. Deep pots accommodate plants with extensive root networks, allowing roots to grow freely and access more nutrients and water. Choosing between shallow and deep pots depends on the specific needs of the plant and its root structure to ensure optimal development.
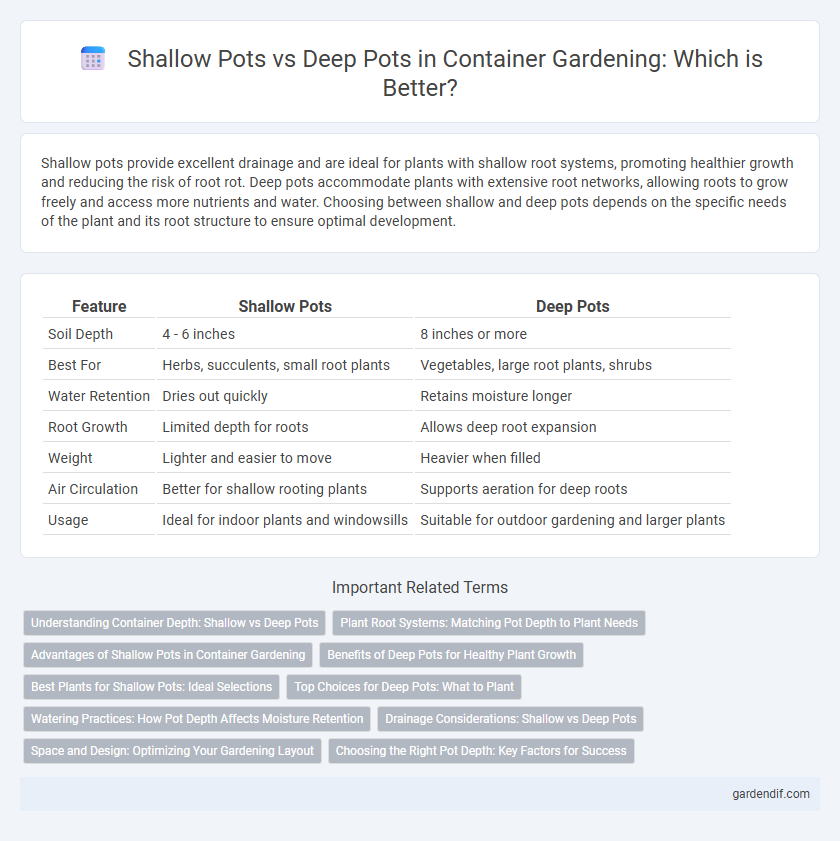
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Shallow Pots | Deep Pots |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Depth | 4 - 6 inches | 8 inches or more |
| Best For | Herbs, succulents, small root plants | Vegetables, large root plants, shrubs |
| Water Retention | Dries out quickly | Retains moisture longer |
| Root Growth | Limited depth for roots | Allows deep root expansion |
| Weight | Lighter and easier to move | Heavier when filled |
| Air Circulation | Better for shallow rooting plants | Supports aeration for deep roots |
| Usage | Ideal for indoor plants and windowsills | Suitable for outdoor gardening and larger plants |
Understanding Container Depth: Shallow vs Deep Pots
Shallow pots offer better air circulation and quicker drainage, making them ideal for plants with shallow root systems or succulents. Deep pots accommodate extensive root growth, supporting larger plants and preventing root binding in species such as tomatoes or shrubs. Selecting the appropriate container depth ensures optimal water retention, root health, and overall plant development.
Plant Root Systems: Matching Pot Depth to Plant Needs
Shallow pots are ideal for plants with fibrous or shallow root systems like herbs and succulents, promoting adequate growth and preventing waterlogging. Deep pots accommodate plants with taproots or extensive root development, such as tomatoes and carrots, ensuring sufficient space for root expansion and nutrient absorption. Matching pot depth to plant root structure optimizes root health, enhances water drainage, and supports overall plant vitality.
Advantages of Shallow Pots in Container Gardening
Shallow pots offer superior drainage and prevent waterlogging, reducing the risk of root rot for container plants. Their compact design allows for greater air circulation around roots, promoting healthier growth in herbs and succulents. These pots are also easier to move and manage on patios or balconies, making them ideal for limited space gardening.
Benefits of Deep Pots for Healthy Plant Growth
Deep pots provide ample space for root expansion, promoting strong and healthy root systems essential for nutrient uptake and stability. They enhance water retention and prevent rapid drying, reducing stress on plants and supporting consistent growth. Deep containers also accommodate larger plants or those with deep-rooted systems, ensuring optimal development and overall plant vitality.
Best Plants for Shallow Pots: Ideal Selections
Best plants for shallow pots include succulents, herbs like thyme and chives, and small leafy greens such as lettuce and spinach, which thrive in limited soil depth. Shallow pots offer excellent drainage and prevent root rot, making them ideal for drought-tolerant species and compact root systems. Selecting plants with shallow root structures ensures optimal growth and reduces the frequency of repotting or watering.
Top Choices for Deep Pots: What to Plant
Deep pots provide ample root space, making them ideal for plants with extensive root systems such as tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants. These containers support deep-rooted herbs like rosemary and thyme, as well as root vegetables like carrots and beets that require greater soil depth for healthy growth. Choosing deep pots for these plants ensures optimal nutrient absorption and stable development, enhancing overall yield and vitality.
Watering Practices: How Pot Depth Affects Moisture Retention
Shallow pots tend to dry out more quickly due to limited soil volume, requiring more frequent watering to maintain adequate moisture levels. Deep pots retain moisture longer as the larger soil mass helps buffer against rapid evaporation and allows roots to access water over an extended period. Gardeners should adjust watering schedules accordingly to prevent overwatering in deep pots and underwatering in shallow containers.
Drainage Considerations: Shallow vs Deep Pots
Shallow pots often require more frequent watering due to limited soil volume and faster drying, making efficient drainage critical to prevent root rot. Deep pots provide greater soil depth for water retention and root expansion but must have well-placed drainage holes to avoid waterlogging at the pot's base. Proper drainage design in both shallow and deep containers ensures healthy root aeration and optimal plant growth.
Space and Design: Optimizing Your Gardening Layout
Shallow pots are ideal for maximizing space in compact gardening layouts, allowing for a denser arrangement of plants with shallow root systems such as herbs and succulents. Deep pots accommodate plants with extensive root growth like tomatoes and peppers, providing stability and nourishment while requiring more vertical space. Choosing between shallow and deep pots strategically enhances garden design efficiency by balancing plant needs and spatial constraints.
Choosing the Right Pot Depth: Key Factors for Success
Selecting the ideal container depth depends on the root structure and growth habits of the plant; shallow pots suit herbs and succulents with shallow root systems, while deep pots accommodate vegetables and flowers that require extensive root development. Proper pot depth ensures optimal drainage, nutrient availability, and aeration, which are critical for healthy plant growth and avoiding root rot. Matching pot depth to plant needs enhances water retention efficiency and overall container gardening success.
Shallow pots vs deep pots Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com