
Self-watering pots vs traditional planters Illustration
Self-watering pots maintain consistent soil moisture through a built-in reservoir, reducing the risk of overwatering and promoting healthier root growth. Traditional planters rely on manual watering, which can lead to uneven moisture levels and increased maintenance. The efficiency of self-watering pots makes them ideal for busy gardeners seeking convenience and optimal plant hydration.
Table of Comparison
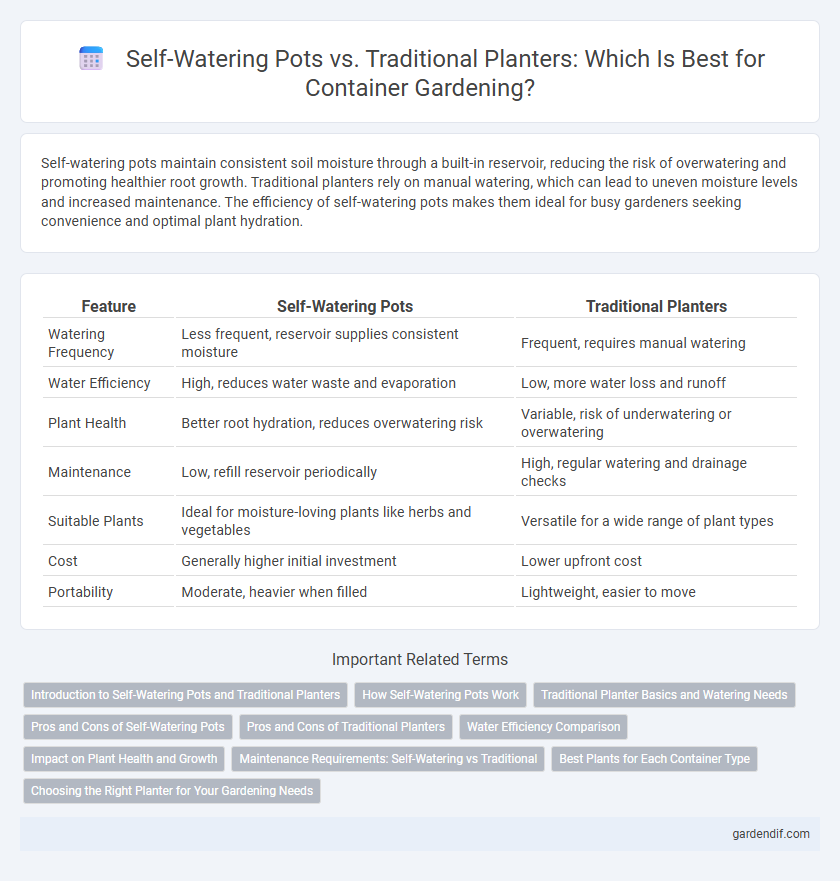
| Feature | Self-Watering Pots | Traditional Planters |
|---|---|---|
| Watering Frequency | Less frequent, reservoir supplies consistent moisture | Frequent, requires manual watering |
| Water Efficiency | High, reduces water waste and evaporation | Low, more water loss and runoff |
| Plant Health | Better root hydration, reduces overwatering risk | Variable, risk of underwatering or overwatering |
| Maintenance | Low, refill reservoir periodically | High, regular watering and drainage checks |
| Suitable Plants | Ideal for moisture-loving plants like herbs and vegetables | Versatile for a wide range of plant types |
| Cost | Generally higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Portability | Moderate, heavier when filled | Lightweight, easier to move |
Introduction to Self-Watering Pots and Traditional Planters
Self-watering pots feature a reservoir at the base that supplies consistent moisture to plants, reducing watering frequency and promoting healthier root growth. Traditional planters rely on manual watering, which can lead to uneven moisture levels and increased risk of under- or overwatering. The design differences impact plant hydration efficiency, maintenance needs, and suitability for various indoor and outdoor gardening environments.
How Self-Watering Pots Work
Self-watering pots operate using a built-in reservoir that supplies water directly to plant roots through capillary action or a wicking system, ensuring consistent moisture levels and reducing overwatering risks. These containers typically feature a soil barrier and water chamber, allowing plants to absorb water as needed, promoting healthier root development and preventing drought stress. Traditional planters lack this mechanism, requiring regular manual watering that can lead to uneven moisture distribution or root rot.
Traditional Planter Basics and Watering Needs
Traditional planters rely on manual watering, requiring regular monitoring to prevent over- or under-watering, which can affect plant health. They typically feature drainage holes to avoid waterlogging, enabling excess water to escape and maintain optimal soil moisture levels. Proper watering frequency depends on the plant species, pot size, and environmental conditions, making attentive care essential for successful growth.
Pros and Cons of Self-Watering Pots
Self-watering pots offer significant advantages such as consistent moisture delivery and reduced watering frequency, which helps prevent root rot and supports healthy plant growth. However, they may cause overwatering in some plant species that require well-drained soil and typically have higher upfront costs compared to traditional planters. These containers are ideal for busy gardeners or those in dry climates but require monitoring to avoid stagnant water and algae buildup.
Pros and Cons of Traditional Planters
Traditional planters offer versatility in size, shape, and materials, providing an aesthetically diverse option for various plant types and decor styles. They require regular manual watering, which can lead to inconsistent moisture levels and potential overwatering or underwatering. While generally more affordable upfront, traditional planters demand more maintenance and attention to plant hydration compared to self-watering pots.
Water Efficiency Comparison
Self-watering pots significantly enhance water efficiency by reducing evaporation and runoff through their reservoir systems, which supply consistent moisture directly to plant roots. Traditional planters often require frequent watering, leading to greater water loss and inconsistent moisture levels. Studies indicate self-watering containers can save up to 50% more water compared to conventional pots, promoting sustainable gardening practices.
Impact on Plant Health and Growth
Self-watering pots enhance plant health by maintaining consistent soil moisture, reducing the risk of overwatering or underwatering common in traditional planters. This steady water supply promotes stronger root development and faster growth, as plants receive optimal hydration without stress. In contrast, traditional planters often require more frequent monitoring and can lead to fluctuating soil dryness, negatively impacting plant vitality and yield.
Maintenance Requirements: Self-Watering vs Traditional
Self-watering pots significantly reduce maintenance by providing consistent moisture through a built-in reservoir, minimizing the frequency of watering compared to traditional planters that require daily or frequent manual irrigation. These containers help prevent overwatering and root rot by regulating water uptake, making them ideal for busy gardeners or those new to plant care. Traditional planters demand diligent monitoring of soil moisture and adjusting watering schedules based on plant species and environmental conditions.
Best Plants for Each Container Type
Self-watering pots are ideal for moisture-loving plants such as herbs, ferns, and peace lilies, which benefit from consistent hydration through a built-in reservoir system. Traditional planters suit drought-tolerant plants like succulents, cacti, and Mediterranean herbs that require well-drained soil and less frequent watering. Matching the container type to the plant's water needs enhances growth efficiency and reduces maintenance efforts.
Choosing the Right Planter for Your Gardening Needs
Self-watering pots provide consistent moisture by using a built-in reservoir that reduces the risk of overwatering and promotes healthier root growth, making them ideal for busy gardeners or plants requiring steady hydration. Traditional planters offer more control over soil type and drainage customization, benefiting plants with specific watering needs or those sensitive to excess moisture. Selecting the right planter depends on factors such as plant species, watering frequency, and environmental conditions to optimize growth and ease of care.
Self-watering pots vs traditional planters Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com