
Plastic containers vs clay containers Illustration
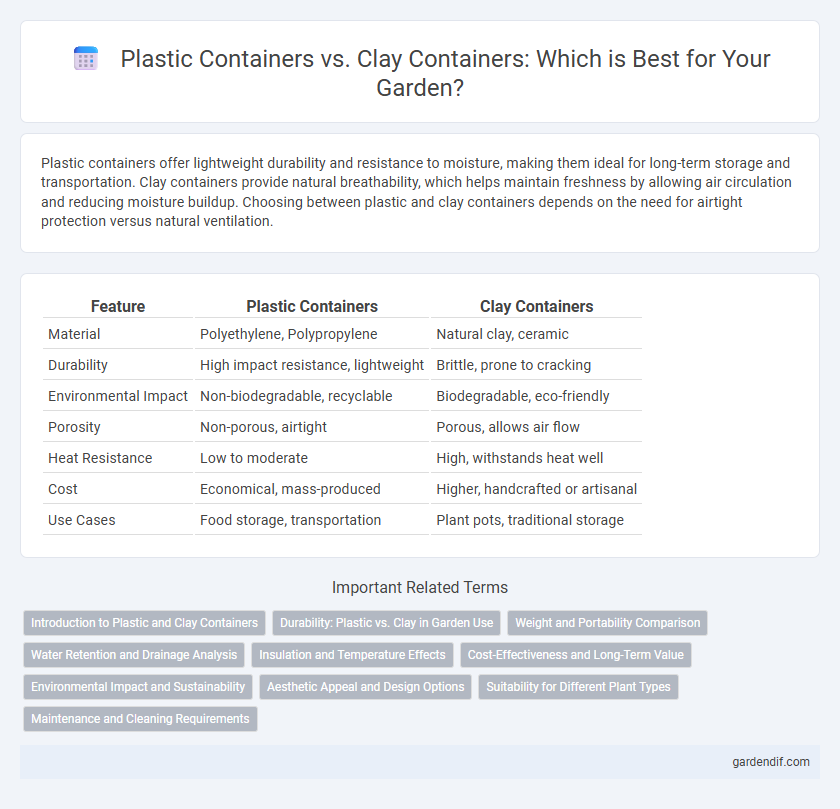
Plastic containers offer lightweight durability and resistance to moisture, making them ideal for long-term storage and transportation. Clay containers provide natural breathability, which helps maintain freshness by allowing air circulation and reducing moisture buildup. Choosing between plastic and clay containers depends on the need for airtight protection versus natural ventilation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plastic Containers | Clay Containers |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Polyethylene, Polypropylene | Natural clay, ceramic |
| Durability | High impact resistance, lightweight | Brittle, prone to cracking |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable | Biodegradable, eco-friendly |
| Porosity | Non-porous, airtight | Porous, allows air flow |
| Heat Resistance | Low to moderate | High, withstands heat well |
| Cost | Economical, mass-produced | Higher, handcrafted or artisanal |
| Use Cases | Food storage, transportation | Plant pots, traditional storage |
Introduction to Plastic and Clay Containers
Plastic containers offer lightweight, durable, and moisture-resistant solutions ideal for food storage and transportation. Clay containers, made from natural earthen materials, provide excellent breathability and temperature regulation, enhancing the freshness of stored items. Each type has unique properties influencing their suitability for different storage needs and environmental conditions.
Durability: Plastic vs. Clay in Garden Use
Plastic containers offer superior durability in garden use due to their resistance to weathering, cracking, and impact compared to clay containers. Clay containers, while aesthetically pleasing, are more vulnerable to breakage from frost and physical damage, making them less suitable for harsh outdoor conditions. Gardeners prioritizing longevity and low maintenance often prefer plastic containers for their robustness and lightweight properties.
Weight and Portability Comparison
Plastic containers are significantly lighter than clay containers, making them more portable and easier to handle during transportation. The lightweight nature of plastic reduces shipping costs and enhances convenience for everyday use, whereas clay containers, though sturdy, tend to be bulky and heavy. This weight difference impacts user preference in scenarios requiring frequent movement or travel.
Water Retention and Drainage Analysis
Plastic containers offer superior water retention due to their non-porous surfaces, preventing moisture loss and maintaining consistent soil hydration. Clay containers, made from porous terracotta, allow for better drainage and air circulation but can lead to faster drying of soil. The choice between plastic and clay containers depends on plant species' water needs and the environmental conditions influencing moisture management.
Insulation and Temperature Effects
Plastic containers offer moderate insulation but can retain heat unevenly, potentially affecting the stored contents' temperature stability. Clay containers provide superior insulation due to their natural porous structure, allowing better temperature regulation and moisture retention. This characteristic makes clay containers ideal for keeping food fresh and cool over extended periods compared to plastic alternatives.
Cost-Effectiveness and Long-Term Value
Plastic containers offer lower upfront costs and lightweight durability, making them cost-effective for short-term storage and frequent transportation. Clay containers, while more expensive initially, provide superior long-term value through enhanced breathability, natural insulation, and biodegradability, which extends the freshness of stored goods and reduces environmental impact. Choosing between plastic and clay containers depends on balancing immediate budget constraints with sustainability goals and product longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Plastic containers contribute significantly to environmental pollution due to their non-biodegradable nature and reliance on fossil fuels, leading to high carbon emissions during production and disposal. Clay containers, made from natural materials, offer greater sustainability through biodegradability and minimal energy use in manufacturing, although their fragility and resource extraction can impact ecosystems. Choosing clay over plastic reduces long-term waste accumulation and supports eco-friendly practices by encouraging the use of renewable resources and soil-friendly disposal methods.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Plastic containers offer a wide range of vibrant colors, shapes, and finishes, allowing for versatile design options that suit modern and practical aesthetics. Clay containers provide a natural, earthy look with unique textures and handcrafted appeal, enhancing rustic or traditional decor styles. While plastic favors uniformity and mass production, clay stands out for its artisanal charm and organic aesthetic appeal.
Suitability for Different Plant Types
Plastic containers offer lightweight durability and excellent moisture retention, making them ideal for moisture-loving plants like ferns and herbs. Clay containers provide superior breathability and drainage, which benefits succulents and cacti by preventing root rot and promoting healthy growth. Selecting the appropriate container type enhances plant health by matching material properties to specific plant water and aeration needs.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Plastic containers require minimal maintenance, as they are non-porous and resistant to stains and odors, making cleaning quick and efficient with soap and water. Clay containers, being porous, necessitate more careful cleaning to prevent moisture absorption and potential mold growth, often requiring thorough drying before reuse. Proper maintenance of clay containers includes occasional oiling to maintain surface integrity, whereas plastic containers generally do not need such treatments.
Plastic containers vs clay containers Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com