
Nitrogen-fixing vs nutrient-extracting Illustration
Companion plants that are nitrogen-fixing enrich the soil by converting atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form, enhancing soil fertility naturally. In contrast, nutrient-extracting plants absorb minerals and nutrients from the soil, which can deplete resources if not managed properly. Balancing nitrogen-fixing and nutrient-extracting companions promotes healthier soil and robust plant growth in sustainable gardening.
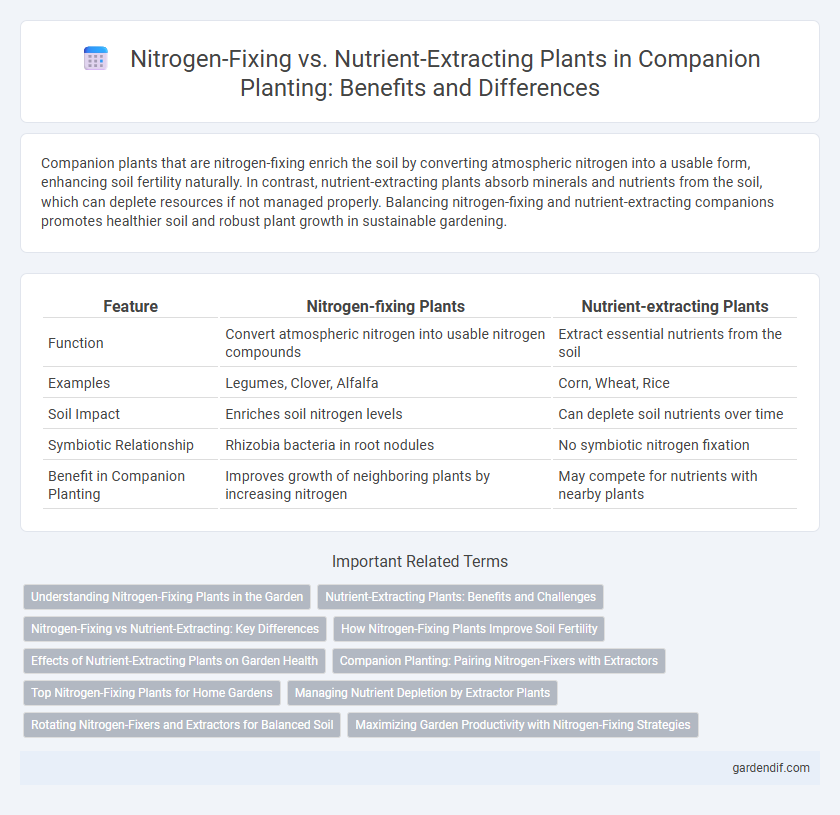
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nitrogen-fixing Plants | Nutrient-extracting Plants |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Convert atmospheric nitrogen into usable nitrogen compounds | Extract essential nutrients from the soil |
| Examples | Legumes, Clover, Alfalfa | Corn, Wheat, Rice |
| Soil Impact | Enriches soil nitrogen levels | Can deplete soil nutrients over time |
| Symbiotic Relationship | Rhizobia bacteria in root nodules | No symbiotic nitrogen fixation |
| Benefit in Companion Planting | Improves growth of neighboring plants by increasing nitrogen | May compete for nutrients with nearby plants |
Understanding Nitrogen-Fixing Plants in the Garden
Nitrogen-fixing plants, such as legumes, form symbiotic relationships with Rhizobium bacteria to convert atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form for soil enrichment, enhancing garden fertility naturally. These plants reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers by replenishing nitrogen levels, promoting healthier growth for companion plants. Understanding their role helps gardeners optimize plant pairing and soil management for sustainable cultivation.
Nutrient-Extracting Plants: Benefits and Challenges
Nutrient-extracting plants play a crucial role in companion planting by drawing essential minerals and nutrients from the soil, supporting the growth of neighboring crops. These plants enhance soil fertility through deep-root systems that access nutrients unavailable to shallow-rooted species, promoting healthier garden ecosystems. Challenges include managing their aggressive nutrient uptake to prevent depletion, requiring careful planning to maintain balanced soil nutrition.
Nitrogen-Fixing vs Nutrient-Extracting: Key Differences
Nitrogen-fixing plants, such as legumes, form symbiotic relationships with Rhizobium bacteria to convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, enriching soil fertility without depleting nutrients. Nutrient-extracting plants draw essential minerals directly from the soil, which may reduce soil nutrient levels if not managed properly. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing companion planting strategies to improve crop yield and maintain soil health.
How Nitrogen-Fixing Plants Improve Soil Fertility
Nitrogen-fixing plants, such as legumes, enhance soil fertility by converting atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia through symbiotic bacteria in their root nodules, making nitrogen available for plant uptake. This natural process enriches soil nitrogen content without the need for synthetic fertilizers, promoting healthier companion crops and increased yields. Their ability to replenish soil nitrogen supports sustainable agriculture by reducing nutrient extraction and maintaining soil balance.
Effects of Nutrient-Extracting Plants on Garden Health
Nutrient-extracting plants can deplete essential soil nutrients, leading to reduced fertility and diminished garden health over time. These plants often compete aggressively with companion plants for nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which can stunt growth and lower crop yields. Maintaining soil balance by monitoring nutrient levels and incorporating nitrogen-fixing companions helps mitigate the negative impact of nutrient-extractors on garden ecosystems.
Companion Planting: Pairing Nitrogen-Fixers with Extractors
Companion planting strategically pairs nitrogen-fixing plants like legumes with nutrient-extracting crops to enhance soil fertility and optimize nutrient uptake. Nitrogen-fixers convert atmospheric nitrogen into forms usable by plants, directly enriching the soil, while nutrient-extractors such as corn and tomatoes absorb essential minerals, benefiting from improved nitrogen availability. This symbiotic relationship minimizes fertilizer dependency and promotes sustainable agricultural ecosystems with balanced nutrient cycles.
Top Nitrogen-Fixing Plants for Home Gardens
Top nitrogen-fixing plants for home gardens include legumes like clover, peas, and beans, which enhance soil fertility by converting atmospheric nitrogen into forms usable by other plants. These companion plants reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers and promote healthier, more productive garden ecosystems. Incorporating nitrogen-fixing species improves nutrient cycling and supports sustainable gardening practices.
Managing Nutrient Depletion by Extractor Plants
Extractor plants rapidly absorb soil nutrients, often leading to nutrient depletion that can hinder surrounding crop growth. Managing nutrient depletion involves strategic crop rotation and incorporating nitrogen-fixing companions, such as legumes, to replenish soil fertility naturally. Regular soil testing and targeted fertilization optimize nutrient availability, balancing the ecosystem between extractor and nitrogen-fixing plants.
Rotating Nitrogen-Fixers and Extractors for Balanced Soil
Rotating nitrogen-fixing plants such as legumes with nutrient-extracting crops like maize promotes balanced soil fertility by replenishing nitrogen while efficiently utilizing other nutrients. This practice enhances soil microbial diversity and prevents nutrient depletion, ensuring sustained crop productivity. Implementing crop rotation strategies with complementary companion plants supports long-term soil health and ecosystem stability.
Maximizing Garden Productivity with Nitrogen-Fixing Strategies
Nitrogen-fixing plants like clover, beans, and peas enhance soil fertility by converting atmospheric nitrogen into forms accessible to other garden plants, boosting overall productivity. Integrating these companions with nutrient-extracting crops such as corn or tomatoes creates a symbiotic balance that reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers. Employing nitrogen-fixing strategies in garden planning significantly improves nutrient cycling and supports sustainable, high-yield growth.
Nitrogen-fixing vs nutrient-extracting Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com