
Guild planting vs single-species beds Illustration
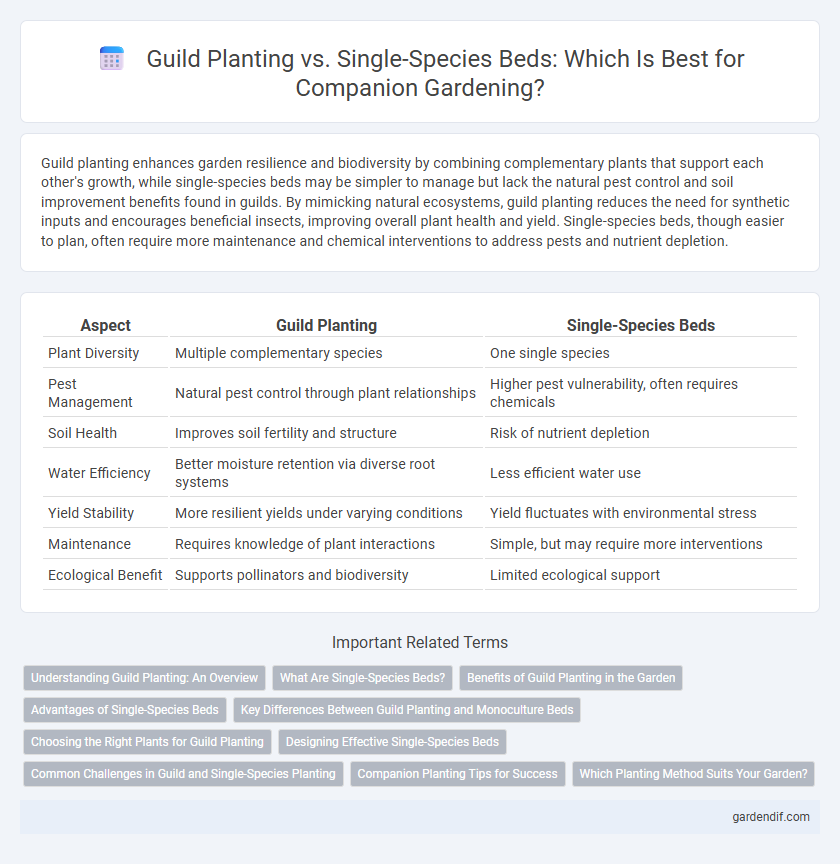
Guild planting enhances garden resilience and biodiversity by combining complementary plants that support each other's growth, while single-species beds may be simpler to manage but lack the natural pest control and soil improvement benefits found in guilds. By mimicking natural ecosystems, guild planting reduces the need for synthetic inputs and encourages beneficial insects, improving overall plant health and yield. Single-species beds, though easier to plan, often require more maintenance and chemical interventions to address pests and nutrient depletion.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Guild Planting | Single-Species Beds |
|---|---|---|
| Plant Diversity | Multiple complementary species | One single species |
| Pest Management | Natural pest control through plant relationships | Higher pest vulnerability, often requires chemicals |
| Soil Health | Improves soil fertility and structure | Risk of nutrient depletion |
| Water Efficiency | Better moisture retention via diverse root systems | Less efficient water use |
| Yield Stability | More resilient yields under varying conditions | Yield fluctuates with environmental stress |
| Maintenance | Requires knowledge of plant interactions | Simple, but may require more interventions |
| Ecological Benefit | Supports pollinators and biodiversity | Limited ecological support |
Understanding Guild Planting: An Overview
Guild planting involves grouping complementary plants to support each other's growth, improving soil health and pest resistance compared to single-species beds. This method leverages natural plant relationships, such as nitrogen-fixing legumes paired with nutrient-demanding vegetables, to create a balanced ecosystem. Enhancing biodiversity within guilds promotes sustainable yields and reduces the need for synthetic inputs.
What Are Single-Species Beds?
Single-species beds are garden plots dedicated exclusively to one type of plant, optimizing growth conditions such as soil nutrients, water, and sunlight specific to that species. These beds simplify pest management by reducing the risk of cross-contamination but may increase vulnerability to species-specific diseases. Unlike guild planting, which combines complementary plants for ecological balance, single-species beds focus on maximizing the yield and health of one crop through specialized care and maintenance.
Benefits of Guild Planting in the Garden
Guild planting enhances garden biodiversity by combining compatible plants that support each other's growth and soil health, leading to increased pest resistance and nutrient cycling. Unlike single-species beds, guild planting maximizes space efficiency and promotes natural habitat for beneficial insects, reducing the need for chemical interventions. This method fosters resilient ecosystems, improves yields, and creates sustainable gardening environments.
Advantages of Single-Species Beds
Single-species beds simplify pest and disease management by allowing targeted treatments and reducing cross-contamination risks. They optimize nutrient uptake as each plant's specific soil requirements are easier to meet, leading to healthier growth and higher yields. Maintenance tasks such as watering, pruning, and harvesting become more efficient due to uniform growth habits and care needs.
Key Differences Between Guild Planting and Monoculture Beds
Guild planting integrates diverse plant species to create a mutually beneficial ecosystem, enhancing soil health, pest control, and nutrient cycling. Monoculture beds focus on cultivating a single species, often leading to higher vulnerability to pests, diseases, and soil depletion due to lack of biodiversity. The primary difference lies in biodiversity-driven resilience and ecosystem support found in guild planting versus the simplicity and efficiency of monoculture for large-scale crop production.
Choosing the Right Plants for Guild Planting
Selecting the right plants for guild planting involves combining species that support each other's growth through complementary functions such as nitrogen fixation, pest control, and pollination attraction. Incorporating nitrogen-fixing plants like clover or beans alongside nutrient-demanding crops enhances soil fertility naturally while dynamic accumulators like comfrey improve nutrient cycling. Unlike single-species beds, guild planting fosters biodiversity, resilience, and sustainable productivity by mimicking natural ecosystems and optimizing resource use.
Designing Effective Single-Species Beds
Designing effective single-species beds requires precise consideration of soil conditions, spacing, and resource allocation to maximize plant health and yield. Uniform planting maximizes nutrient uptake efficiency and simplifies pest management compared to the complexity of guild planting. Optimal bed design includes appropriate row orientation for sunlight exposure and consistent watering systems to support robust growth.
Common Challenges in Guild and Single-Species Planting
Guild planting often faces challenges such as managing complex interactions between multiple species, which can lead to competition for nutrients, water, and light, increasing the difficulty of maintaining balance within the system. Single-species beds typically encounter issues like pest infestations and nutrient depletion due to the lack of biodiversity and monoculture vulnerabilities. Both approaches require tailored strategies for soil health, pest control, and resource allocation to optimize plant growth and yield.
Companion Planting Tips for Success
Guild planting enhances garden health by combining complementary plants that support each other's growth, pest resistance, and nutrient uptake, unlike single-species beds which lack this synergy. Strategically pairing nitrogen-fixing plants like clover, pest-repelling herbs such as basil, and deep-rooted plants can improve soil fertility and reduce pest pressures naturally. Successful companion planting requires understanding plant relationships, spacing for airflow, and rotating guild components seasonally to maintain soil balance and maximize yields.
Which Planting Method Suits Your Garden?
Guild planting integrates diverse plant species that mutually support growth, pest control, and soil health, making it ideal for gardeners seeking sustainable and resilient ecosystems. Single-species beds simplify management and harvesting, offering uniform growth conditions best suited for gardeners focused on maximizing yield and neatness. Selecting between guild planting and single-species beds depends on your garden's size, maintenance capacity, and goals for biodiversity or productivity.
Guild planting vs single-species beds Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com