
Dynamic accumulators vs nutrient depleters Illustration
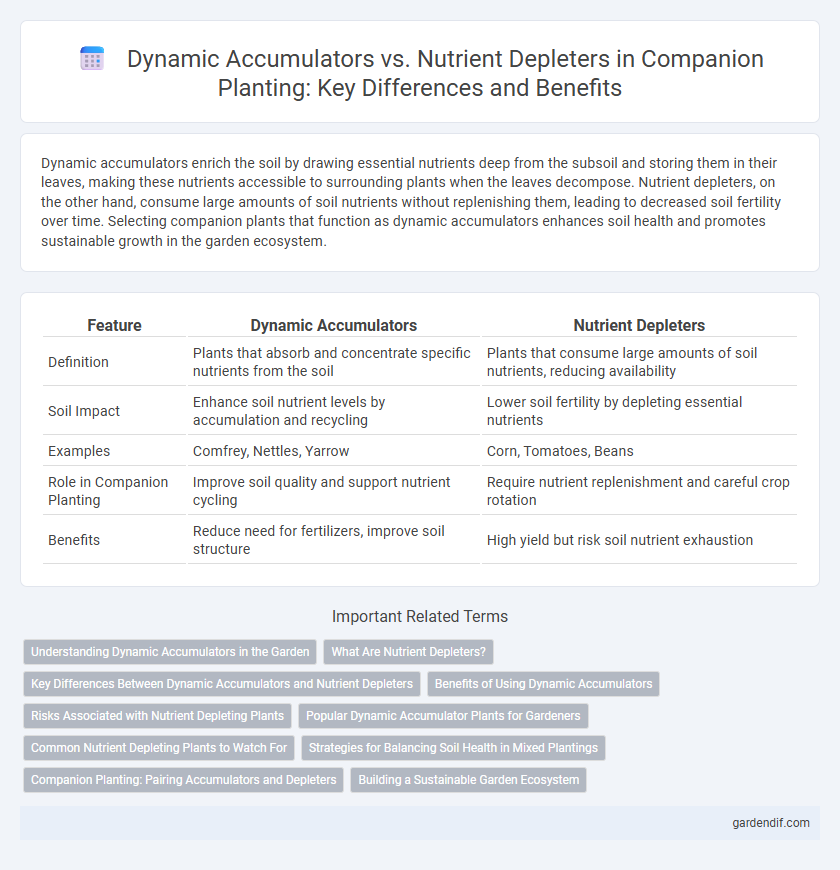
Dynamic accumulators enrich the soil by drawing essential nutrients deep from the subsoil and storing them in their leaves, making these nutrients accessible to surrounding plants when the leaves decompose. Nutrient depleters, on the other hand, consume large amounts of soil nutrients without replenishing them, leading to decreased soil fertility over time. Selecting companion plants that function as dynamic accumulators enhances soil health and promotes sustainable growth in the garden ecosystem.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dynamic Accumulators | Nutrient Depleters |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Plants that absorb and concentrate specific nutrients from the soil | Plants that consume large amounts of soil nutrients, reducing availability |
| Soil Impact | Enhance soil nutrient levels by accumulation and recycling | Lower soil fertility by depleting essential nutrients |
| Examples | Comfrey, Nettles, Yarrow | Corn, Tomatoes, Beans |
| Role in Companion Planting | Improve soil quality and support nutrient cycling | Require nutrient replenishment and careful crop rotation |
| Benefits | Reduce need for fertilizers, improve soil structure | High yield but risk soil nutrient exhaustion |
Understanding Dynamic Accumulators in the Garden
Dynamic accumulators are plants that absorb and concentrate essential nutrients from the soil into their leaves and roots, making them valuable for enriching garden soils naturally. Unlike nutrient depleters, which extract and diminish soil fertility, dynamic accumulators help cycle nutrients by bringing deep or less accessible minerals to the surface for other plants to utilize. Key examples include comfrey, nettle, and yarrow, which improve soil health and support companion planting strategies for sustainable gardening.
What Are Nutrient Depleters?
Nutrient depleters are plants that absorb large amounts of soil nutrients, reducing the availability of essential minerals for surrounding plants. These species often require frequent fertilization to maintain soil fertility and prevent nutrient exhaustion. Understanding the role of nutrient depleters is crucial for effective companion planting and sustainable garden management.
Key Differences Between Dynamic Accumulators and Nutrient Depleters
Dynamic accumulators are plants that absorb and concentrate specific nutrients from the soil, making them valuable for improving soil fertility and providing essential minerals to companion plants. Nutrient depleters, on the other hand, extract large amounts of nutrients without returning them to the soil, potentially leading to diminished soil quality and reduced plant growth. Understanding these key differences helps gardeners select appropriate companion plants to enhance soil health and optimize garden productivity.
Benefits of Using Dynamic Accumulators
Dynamic accumulators enhance soil health by drawing up essential nutrients like potassium, calcium, and trace minerals from deep soil layers, making them accessible to neighboring plants. Their use reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers and promotes a balanced nutrient cycle, boosting overall garden productivity and plant resilience. Incorporating these plants in companion planting supports sustainable agriculture and improves crop yield quality.
Risks Associated with Nutrient Depleting Plants
Nutrient depleting plants pose significant risks by exhausting soil essential minerals such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, leading to reduced fertility and compromised growth of companion plants. Prolonged cultivation of these species can result in nutrient imbalances, increased susceptibility to pests and diseases, and long-term degradation of soil structure. Managing dynamic accumulators in companion planting helps replenish vital nutrients, supporting sustainable soil health and optimizing overall plant productivity.
Popular Dynamic Accumulator Plants for Gardeners
Popular dynamic accumulator plants for gardeners include comfrey, dandelion, and yarrow, known for drawing essential nutrients like potassium, calcium, and phosphorus from deep soil layers. These plants improve soil fertility by accumulating minerals that benefit neighboring crops without depleting surface nutrients. Integrating dynamic accumulators in companion planting enhances overall garden health and promotes sustainable nutrient cycling.
Common Nutrient Depleting Plants to Watch For
Common nutrient depleting plants such as corn, tomatoes, and potatoes rapidly absorb essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium from the soil, often leading to reduced fertility in companion planting systems. Monitoring these nutrient depleting species is crucial to maintaining balanced soil health, promoting sustainable growth for surrounding companion crops. Implementing dynamic accumulators like comfrey or clover nearby can replenish soil nutrients, counteracting the depletion caused by high-demand plants.
Strategies for Balancing Soil Health in Mixed Plantings
Dynamic accumulators like comfrey and yarrow draw deep soil nutrients such as potassium, calcium, and phosphorus to the surface, enriching topsoil naturally. Nutrient depleters such as corn and tomatoes consume high levels of nitrogen and potassium, potentially depleting soil fertility if planted consecutively. Strategies for balancing soil health in mixed plantings include rotating nutrient depleters with dynamic accumulators and incorporating nitrogen-fixing plants like legumes to maintain optimal nutrient levels and soil structure.
Companion Planting: Pairing Accumulators and Depleters
Companion planting leverages the balance between dynamic accumulators, which draw up nutrients like nitrogen and minerals from deep soil layers, and nutrient depleters, which consume these nutrients rapidly. Pairing accumulators such as comfrey or yarrow with heavy feeders like tomatoes or corn enhances soil fertility while maximizing plant health and yields. This strategic planting reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers and promotes sustainable garden ecosystems.
Building a Sustainable Garden Ecosystem
Dynamic accumulators are plants that absorb and concentrate key nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium from deep in the soil, making them available for neighboring plants when their leaves decompose. Nutrient depleters, on the other hand, heavily consume soil nutrients without replenishing them, potentially leading to soil degradation over time. Incorporating dynamic accumulators into a garden ecosystem helps maintain soil fertility, supports plant health, and fosters a sustainable, balanced environment.
Dynamic accumulators vs nutrient depleters Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com