
Alley cropping vs Strip cropping Illustration
Alley cropping integrates rows of trees with crops planted in between, enhancing biodiversity and soil fertility while providing shade and wind protection. Strip cropping alternates strips of different crops to reduce soil erosion and improve moisture retention on sloped land. Both methods promote sustainable agriculture but differ in spatial arrangement and primary environmental benefits.
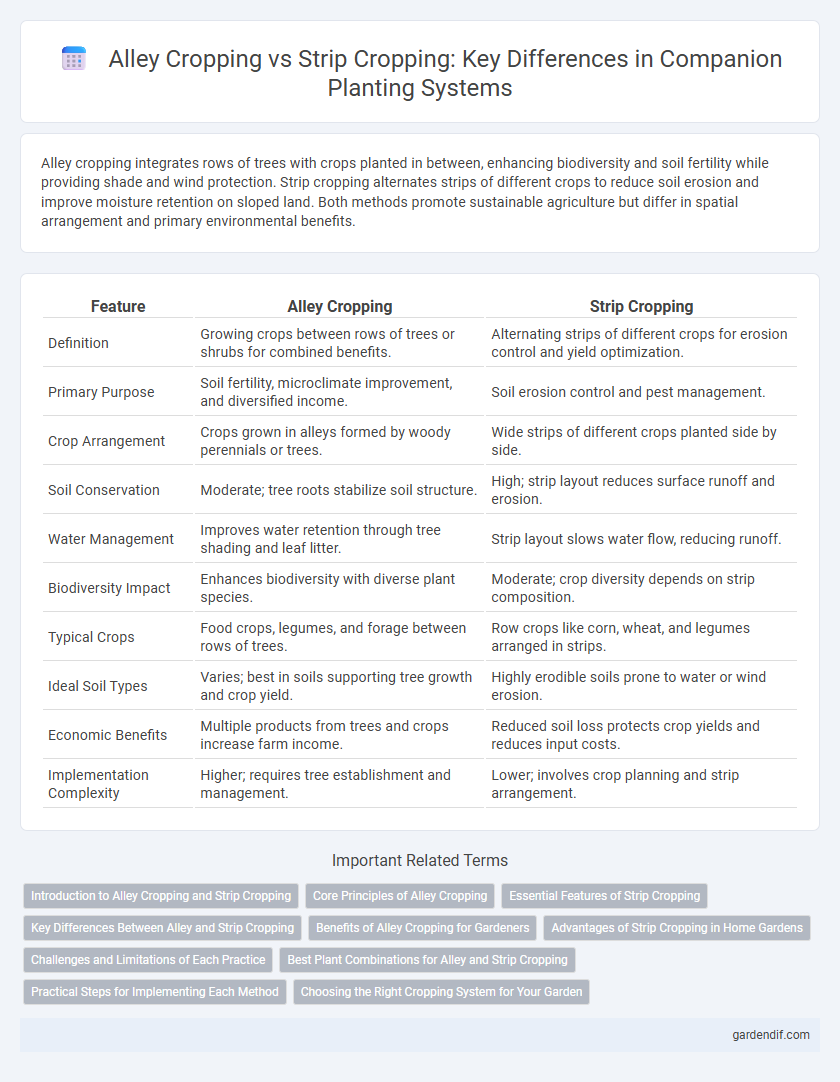
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Alley Cropping | Strip Cropping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Growing crops between rows of trees or shrubs for combined benefits. | Alternating strips of different crops for erosion control and yield optimization. |
| Primary Purpose | Soil fertility, microclimate improvement, and diversified income. | Soil erosion control and pest management. |
| Crop Arrangement | Crops grown in alleys formed by woody perennials or trees. | Wide strips of different crops planted side by side. |
| Soil Conservation | Moderate; tree roots stabilize soil structure. | High; strip layout reduces surface runoff and erosion. |
| Water Management | Improves water retention through tree shading and leaf litter. | Strip layout slows water flow, reducing runoff. |
| Biodiversity Impact | Enhances biodiversity with diverse plant species. | Moderate; crop diversity depends on strip composition. |
| Typical Crops | Food crops, legumes, and forage between rows of trees. | Row crops like corn, wheat, and legumes arranged in strips. |
| Ideal Soil Types | Varies; best in soils supporting tree growth and crop yield. | Highly erodible soils prone to water or wind erosion. |
| Economic Benefits | Multiple products from trees and crops increase farm income. | Reduced soil loss protects crop yields and reduces input costs. |
| Implementation Complexity | Higher; requires tree establishment and management. | Lower; involves crop planning and strip arrangement. |
Introduction to Alley Cropping and Strip Cropping
Alley cropping integrates rows of trees or shrubs with agricultural crops grown in the spaces between, enhancing biodiversity and soil quality while providing economic benefits from both timber and crops. Strip cropping involves cultivating alternating strips of different crops, typically along the contour of the land, to reduce soil erosion and improve water retention. Both practices promote sustainable land management by combining vegetation and crop production to optimize resource use and environmental health.
Core Principles of Alley Cropping
Alley cropping integrates rows of trees with agricultural crops or pasture in alternating strips, optimizing land use and enhancing biodiversity. Core principles emphasize selecting compatible tree and crop species to create mutual benefits like improved soil fertility, microclimate moderation, and pest control. This method supports sustainable agroforestry by balancing economic productivity with ecological resilience.
Essential Features of Strip Cropping
Strip cropping involves planting alternating strips of crops, typically row crops with cover crops, to reduce soil erosion and improve moisture retention. Essential features include the strategic alignment of strips along the contour lines, usage of permanent cover crops to protect the soil, and the width of strips adjusted to crop type and slope gradient. This method enhances soil fertility, supports pest management, and increases overall crop productivity by maintaining the ecological balance in companion planting systems.
Key Differences Between Alley and Strip Cropping
Alley cropping integrates rows of trees or shrubs between crop alleys, enhancing biodiversity and soil fertility through root interactions and organic matter accumulation. Strip cropping alternates strips of different crops, primarily to reduce soil erosion and manage water runoff by creating physical barriers. The key differences lie in alley cropping's use of perennial woody plants for microclimate control and long-term nutrient cycling, whereas strip cropping relies on spatial crop rotation to optimize pest control and soil conservation.
Benefits of Alley Cropping for Gardeners
Alley cropping enhances soil fertility and moisture retention by integrating nitrogen-fixing trees or shrubs alongside crops, promoting healthier plant growth and higher yields for gardeners. This method provides natural pest control by attracting beneficial insects and creating a diverse ecosystem, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Gardeners also benefit from improved microclimates and wind protection, which fosters more resilient crops and sustainable gardening practices.
Advantages of Strip Cropping in Home Gardens
Strip cropping in home gardens enhances soil erosion control by alternating crops with different root structures, improving water retention and nutrient cycling. This method increases biodiversity by supporting various pests and beneficial insects, which naturally reduce pest populations. Strip cropping also optimizes space usage, allowing gardeners to maximize yield and maintain healthier, more resilient garden ecosystems.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Practice
Alley cropping faces challenges such as root competition and shading, which can limit crop growth and reduce overall yield. Strip cropping struggles with soil erosion control when strips are not properly maintained and may require precise management to avoid pest infestations. Both practices demand careful planning to balance resource use and maximize productivity while mitigating environmental impacts.
Best Plant Combinations for Alley and Strip Cropping
Alley cropping thrives with deep-rooted trees like nitrogen-fixing black locust paired with shallow-rooted crops such as maize, optimizing nutrient cycling and soil structure. Strip cropping excels by alternating strips of cereal grains like wheat with leguminous crops such as soybeans to reduce erosion and enhance soil fertility. Selecting complementary plant species based on root depth, nutrient requirements, and growth habits maximizes productivity and sustainability in both systems.
Practical Steps for Implementing Each Method
Alley cropping involves planting rows of trees with crops grown in the alleys between, requiring careful selection of tree species and crops that complement each other's root and nutrient needs, plus installation of irrigation systems to support both layers. Strip cropping alternates strips of different crops to reduce soil erosion and improve fertility, demanding precise field layout, contour planting techniques, and timely management of strip sequences to maximize yield and soil health. Both methods benefit from soil testing, ongoing monitoring, and adaptive management to optimize plant growth and resource use.
Choosing the Right Cropping System for Your Garden
Alley cropping integrates rows of trees with crops, enhancing biodiversity and improving soil fertility through natural nitrogen fixation and shading benefits. Strip cropping involves alternating strips of different crops to control erosion and maximize land use efficiency, especially on sloped terrain. Selecting the right system depends on your garden's space, climate, and crop compatibility to optimize yield and sustainability.
Alley cropping vs Strip cropping Infographic
 gardendif.com
gardendif.com